Eye test how long? This question is surprisingly complex, encompassing a wide range of factors influencing the duration of an eye examination. From routine check-ups to specialized diagnostic procedures, the time commitment varies significantly. This guide delves into the specifics of various eye tests, exploring the contributing factors that determine their length and offering practical advice for patients to optimize their appointment experience.
Understanding the duration of different eye tests is crucial for effective time management and realistic expectations. We will examine the types of tests, the influence of patient factors (age, health, cooperation), and the impact of technological advancements on the overall examination time. This comprehensive overview aims to equip readers with the knowledge to navigate the process with confidence and preparedness.
Types of Eye Tests and Duration
Comprehensive eye exams are crucial for maintaining good vision and detecting potential eye diseases. The duration of these exams, and the individual tests within them, can vary depending on several factors. This section details common eye tests, their typical durations, and the elements influencing those durations.
Common Eye Tests and Their Durations
The following table summarizes common eye tests and their average durations. It’s important to note that these are estimates, and the actual time spent on each test can vary considerably depending on individual patient needs and the specific equipment used.
| Test Name | Description | Average Duration | Factors Affecting Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Acuity Test | Measures how clearly you see at various distances using an eye chart. | 5-10 minutes | Patient cooperation, presence of refractive errors, need for repeat testing with different corrections. |
| Refraction | Determines the refractive error (nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism) and the prescription for corrective lenses. | 15-30 minutes | Complexity of refractive error, patient’s ability to provide accurate responses, need for adjustments during the procedure. |
| Cover Test | Assesses eye alignment and the presence of strabismus (crossed eyes). | 5-10 minutes | Patient’s age and ability to follow instructions, presence of significant eye misalignment. |
| Pupil Dilation | Dilates the pupils to allow for a more thorough examination of the internal structures of the eye. | 10-15 minutes (plus additional time for the subsequent exam) | Pupil dilation response, need for additional time for the ophthalmoscopy following dilation. |
| Ophthalmoscopy (Fundus Examination) | Examines the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels at the back of the eye. | 10-20 minutes | Patient’s pupil dilation, presence of eye conditions requiring more detailed examination, use of specialized imaging techniques. |
| Tonometry | Measures intraocular pressure (IOP) to screen for glaucoma. | 5 minutes | Patient cooperation, accuracy of measurements, need for repeat measurements. |
| Visual Field Test | Assesses the extent of your peripheral vision. | 15-30 minutes | Patient’s attention span, presence of visual field defects, complexity of the test. |
| Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) | Creates detailed cross-sectional images of the retina and optic nerve. | 10-15 minutes | Image quality, need for multiple scans, complexity of findings. |
Differences in Duration Between Comprehensive and Specialized Eye Exams
A comprehensive eye exam typically includes a combination of the tests listed above and takes between 45 minutes to an hour or more. Specialized eye tests, such as those focusing on specific conditions like glaucoma or macular degeneration, may be shorter if they concentrate on a single aspect of eye health. For example, a glaucoma screening might only involve tonometry and visual field testing, taking significantly less time than a complete comprehensive exam.
Conversely, a detailed evaluation for diabetic retinopathy could take longer due to the need for extensive retinal imaging and analysis. The duration therefore is highly dependent on the purpose and scope of the examination.
Factors Affecting Eye Test Length
The duration of a comprehensive eye examination varies significantly depending on several interacting factors. These factors can be broadly categorized into patient-related characteristics and the complexity of the case itself. Understanding these influences helps patients manage their expectations and ophthalmologists optimize their scheduling.Patient characteristics significantly impact examination time. Age, overall health, and the patient’s ability to cooperate during the test all play crucial roles.
For example, young children often require more time and patience due to their limited attention spans and potential reluctance to participate in certain procedures. Similarly, patients with cognitive impairments or physical limitations may need extra time and assistance. Conversely, cooperative adults who clearly understand the instructions generally undergo quicker examinations.
Patient Factors Influencing Examination Time, Eye test how long
The influence of patient factors on eye exam duration is substantial. Elderly patients, for instance, might require more time due to potential age-related conditions affecting vision and manual dexterity. Patients with underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, may necessitate more thorough assessments to detect any related ocular complications. These conditions can manifest as retinopathy, glaucoma, or other eye diseases requiring detailed investigation and longer examination times.
Finally, a patient’s level of cooperation is paramount; a patient who struggles to follow instructions or maintain focus will inevitably prolong the procedure. A patient’s anxiety level also plays a role, sometimes requiring extra time for reassurance and explanation.
Case Complexity and Examination Duration
The complexity of a patient’s case is another major determinant of the eye exam’s length. A routine check-up for a healthy individual with no known vision problems will naturally be shorter than an examination for someone with suspected glaucoma or macular degeneration.
- Routine Eye Exam: A typical routine exam, involving visual acuity testing, refraction, and basic ophthalmoscopy, might take 30-45 minutes.
- Suspected Glaucoma: If glaucoma is suspected, additional tests such as visual field testing, gonioscopy, and optical coherence tomography (OCT) are needed, extending the exam to 1-1.5 hours or more.
- Diabetic Retinopathy Screening: Patients with diabetes require dilated fundus examination, potentially including fluorescein angiography or OCT, significantly increasing the exam time to over an hour.
- Complex Refractive Errors: Individuals with high refractive errors or astigmatism may need more time for precise refraction and lens selection, potentially adding 15-30 minutes to the standard exam.
- Post-Surgical Follow-up: Post-surgical follow-up appointments may involve detailed assessment of healing, potential complications, and adjustments to treatment plans, increasing the examination time depending on the complexity of the procedure.
Routine versus Suspected Eye Conditions: Time Comparison
The time commitment for routine eye exams differs significantly from those involving suspected eye conditions. Routine exams, focusing on refractive error correction and overall eye health assessment, are generally shorter, often completed within 30-45 minutes. Conversely, exams for suspected eye conditions necessitate more extensive testing and often involve the use of specialized equipment, resulting in significantly longer appointment durations, potentially extending to 1-2 hours or more.
The duration of an eye test varies depending on the individual’s needs and the comprehensiveness of the exam. For example, a routine check might take 15-20 minutes, while a more thorough examination could extend longer. Interestingly, the time spent considering color coordination, such as learning how to cobalt blue how to accessorize a royal blue dress , is a different kind of time investment altogether.
Returning to eye tests, remember to always schedule sufficient time for a complete assessment.
The added time is necessary for thorough evaluation and diagnosis to ensure appropriate management and treatment.
Preparation for an Eye Test and Time Management: Eye Test How Long
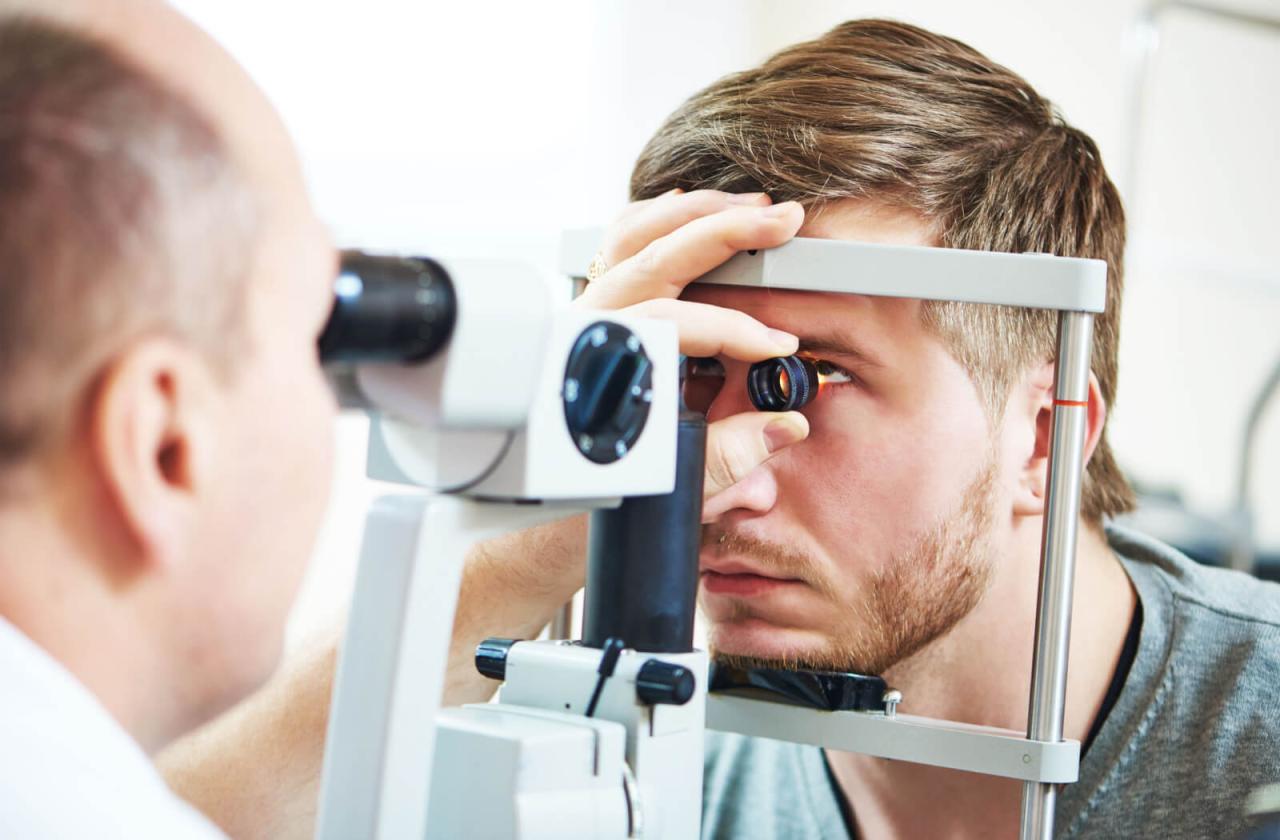
Efficient preparation before an eye examination significantly reduces waiting time and ensures a smoother appointment. Planning ahead allows for a more focused and productive consultation with your ophthalmologist or optometrist. This section details strategies for optimizing your time and maximizing the effectiveness of your eye exam.
Step-by-Step Guide for Minimizing Appointment Waiting Time
Prior preparation is key to a shorter wait. Following these steps can help streamline the process.
- Confirm Appointment Details: Before the day of your appointment, reconfirm the date, time, and location with the eye care provider. This simple step prevents missed appointments and potential delays.
- Complete Paperwork in Advance: Many practices offer online forms that can be completed prior to your visit. This reduces the time spent filling out paperwork in the waiting room.
- Arrive on Time or Slightly Early: Arriving 10-15 minutes early allows for check-in and any unforeseen delays, minimizing your overall wait time. Arriving significantly earlier may not shorten your wait, and arriving late could delay your appointment.
- Gather Relevant Information: Compile any relevant information, such as your current prescription, a list of medications, and any family history of eye conditions. Having this information readily available speeds up the consultation.
- Wear Comfortable Clothing: Choose clothing that is easy to remove and put back on, as some eye tests may require adjustments to your attire.
Checklist of Questions Regarding Appointment Duration
Patients should be proactive in understanding the expected time commitment. Asking these questions can provide valuable insight into appointment length.
- What is the estimated duration of the complete eye examination?
- Are there any specific tests that might take longer than others?
- Is there any pre-test preparation I need to do that might affect the duration of my appointment?
- What is the typical wait time before seeing the doctor?
- What should I do if I anticipate my appointment running over the allocated time?
Effective Time Management Around an Eye Exam Appointment
Managing time effectively around an eye exam requires planning and consideration of potential delays.Scheduling the appointment at a time that minimizes disruption to your daily routine is crucial. For example, scheduling an appointment during a lunch break might be less disruptive than scheduling during peak work hours. If the appointment requires significant travel time, consider adjusting your schedule to account for potential traffic or transportation delays.
Furthermore, arranging for childcare or other necessary support before the appointment can ensure a stress-free experience. If the appointment is expected to take a longer duration, consider arranging for tasks to be completed before or after the appointment. For instance, if the appointment is in the afternoon, you may want to schedule errands or meetings in the morning.
This approach minimizes disruptions and improves efficiency.
Technological Advancements and Eye Test Duration

Technological advancements in ophthalmology have significantly reduced the time required for comprehensive eye examinations. The integration of automated systems and sophisticated imaging techniques has streamlined various aspects of the testing process, leading to faster and more efficient assessments. This has improved patient flow in clinics and allowed ophthalmologists to see more patients within a given timeframe.The shift from traditional methods to newer technologies has dramatically altered the duration of eye tests.
Traditional methods often involved lengthy manual procedures, such as manual refraction and visual acuity testing, which could take considerable time. Newer technologies, however, have automated many of these steps, resulting in a significant reduction in overall examination time.
Automated Refraction and Visual Acuity Testing
Automated refraction systems use computer-controlled phoropters to quickly and accurately determine a patient’s refractive error. These systems eliminate the need for manual adjustments by the examiner, significantly reducing the time spent on this crucial part of the eye exam. Similarly, automated visual acuity charts and systems provide faster and more objective measurements of visual acuity compared to traditional Snellen charts, which rely on subjective patient responses.
For example, a traditional refraction process might take 10-15 minutes, while automated systems can complete the same process in 2-5 minutes.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and its Impact
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique that provides high-resolution cross-sectional images of the retina and optic nerve. While traditional methods of retinal examination relied heavily on ophthalmoscopy, a manual and time-consuming process, OCT provides detailed images in a matter of seconds. This allows for faster detection of retinal diseases and conditions, such as macular degeneration and glaucoma, leading to quicker diagnoses and treatment planning.
The speed and detail provided by OCT drastically reduces the time needed for thorough retinal assessment compared to traditional methods. A comprehensive retinal exam using traditional ophthalmoscopy might take 10-15 minutes, while OCT can achieve similar or better results in under 5 minutes.
Automated Perimetry and Visual Field Testing
Automated perimetry systems provide a more efficient and standardized way to assess a patient’s visual field. Traditional perimetry often relied on manual techniques and subjective patient responses, which could be time-consuming and prone to errors. Automated systems use sophisticated algorithms to quickly and accurately map the visual field, identifying any blind spots or areas of reduced vision. This automated approach significantly reduces the time required for visual field testing.
A typical automated perimetry test can be completed in 5-10 minutes, compared to potentially 20-30 minutes or more with manual methods. The automated nature ensures consistency and reduces variability associated with manual testing.
Impact of Automated Systems on Overall Efficiency
The use of automated systems in eye examinations has significantly improved the overall efficiency of the process. By automating several key steps, these systems reduce the time spent on individual tests and allow ophthalmologists to see more patients in a shorter period. This increased efficiency can lead to improved access to eye care, particularly in settings with high patient volume or limited resources.
Moreover, the objective nature of automated systems minimizes inter-examiner variability and enhances the reliability and reproducibility of test results. The reduction in testing time also contributes to reduced patient waiting times and improved patient satisfaction.
Array
This section presents a visual comparison of the average durations of various common eye examinations. A bar chart is the most suitable format to clearly illustrate these differences in time commitment.The bar chart would have “Type of Eye Test” on the horizontal axis and “Average Duration (minutes)” on the vertical axis. Each bar represents a different type of eye test, with its height corresponding to the average time it takes to complete.
For example, a standard comprehensive eye exam, including visual acuity tests, refraction, and assessment of eye health, might be represented by a bar reaching approximately 45 minutes. A simpler vision screening, focusing solely on visual acuity, could be represented by a much shorter bar, perhaps around 10-15 minutes. Other bars could represent specialized tests such as glaucoma screening (approximately 15-20 minutes), macular degeneration testing (20-30 minutes), or contact lens fitting (30-45 minutes).
The specific durations are approximate averages and can vary based on factors discussed below.
Comparison of Time Commitment Across Different Eye Tests
The visual representation clearly highlights the significant differences in time commitment between various eye tests. Comprehensive eye exams, encompassing a broader range of assessments, naturally require considerably more time than simpler vision screenings. Specialized tests, focusing on specific conditions, also tend to take longer than routine examinations due to the more detailed nature of the assessments and equipment involved.
For instance, the bar for a comprehensive exam would be noticeably longer than the bar representing a simple vision screening, illustrating the increased time required for a more thorough evaluation. Similarly, tests for specific conditions, like glaucoma or macular degeneration, would have bars of comparable length to comprehensive exams, reflecting the in-depth nature of those assessments.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating Factors Affecting Eye Test Duration
Imagine a patient, Mr. Jones, undergoing a comprehensive eye exam. Initially, the optometrist anticipates a standard 45-minute appointment. However, during the exam, Mr. Jones reports experiencing blurry vision and discomfort in his left eye.
This necessitates additional tests, such as detailed retinal imaging and assessment of intraocular pressure, prolonging the appointment. Furthermore, Mr. Jones’s pupils dilate slowly, delaying the refraction process. These unforeseen complications add approximately 15-20 minutes to the original estimated duration, resulting in a total appointment time of 65-70 minutes. This scenario illustrates how unexpected findings and individual patient factors can significantly impact the overall length of an eye examination.
Ultimately, the duration of an eye test is highly individualized, depending on several interconnected factors. While routine exams might be relatively brief, more complex situations can necessitate a longer appointment. By understanding these factors and engaging proactively with your eye care professional, you can better manage your time and ensure a thorough and efficient examination. This guide provides a foundation for understanding the process and empowers patients to ask informed questions, leading to a more positive and productive experience.
Essential Questionnaire
What should I bring to my eye exam?
Bring your insurance card, a list of current medications, and a list of questions for your doctor. Sunglasses are also recommended if your eyes are sensitive to light after dilation.
Can I drive myself home after an eye exam with dilation?
Driving after dilation is generally not recommended as it can blur your vision. Arrange for transportation or allow ample time for the effects to wear off before driving.
How often should I have a comprehensive eye exam?
Frequency depends on age, risk factors, and existing eye conditions. Your eye doctor will advise on the appropriate schedule for you.
What if I need to reschedule my appointment?
Contact your eye doctor’s office as soon as possible to reschedule. Most offices have cancellation policies, so it’s important to be aware of those.
