Aquadur test strips how to read – Aquadur test strips: how to read them accurately is crucial for obtaining reliable results. These strips provide a convenient and relatively inexpensive method for measuring various water parameters, depending on the specific type of strip used. Understanding the proper techniques for using and interpreting Aquadur test strips is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of your water quality assessments.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the process, from sample collection to result interpretation, along with troubleshooting tips and safety precautions.
Aquadur test strips are designed for various applications, ranging from monitoring pool water chemistry to analyzing water samples in scientific research. Different types of Aquadur strips exist, each tailored to measure specific parameters such as pH, chlorine, alkalinity, or other relevant water quality indicators. Proper storage is critical to maintain the accuracy and reliability of these strips, as exposure to moisture or extreme temperatures can affect their performance.
The following sections will detail the correct procedures for using Aquadur test strips, interpreting the results, and addressing potential issues.
Understanding Aquadur Test Strips
Aquadur test strips are diagnostic tools used to quickly and easily assess the water quality in various applications. They function by employing a colorimetric method, where specific chemical indicators react with substances in the water, producing a color change that corresponds to the concentration of the target analyte. This allows for a rapid, on-site assessment without the need for complex laboratory equipment.
Aquadur Test Strip Types and Applications
Aquadur offers a range of test strips designed to measure different water quality parameters. The specific type of strip to use depends entirely on the application and the parameter of interest. Choosing the correct strip is crucial for accurate results. Different strips measure different parameters and have different concentration ranges.
Aquadur Test Strip Storage for Accuracy
Proper storage is essential to maintain the accuracy and reliability of Aquadur test strips. Exposure to moisture, extreme temperatures, and direct sunlight can degrade the chemical indicators on the strips, leading to inaccurate readings. To ensure optimal performance, Aquadur test strips should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and excessive humidity. The original container should be tightly sealed after each use to prevent moisture absorption.
Ideally, the storage area should have a stable temperature, ideally between 15°C and 25°C.
Comparison of Aquadur Test Strip Types
The following table compares several common types of Aquadur test strips, outlining their testing ranges and typical applications. Note that specific ranges and applications may vary depending on the manufacturer’s specifications.
| Test Strip Type | Parameter Measured | Testing Range | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aquadur Chlorine Test Strips | Free Chlorine | 0.5 – 5.0 ppm | Swimming pools, spas, water treatment plants |
| Aquadur pH Test Strips | pH | 6.0 – 8.0 | Aquariums, hydroponics, water treatment plants |
| Aquadur Hardness Test Strips | Water Hardness (as CaCO3) | 50 – 500 ppm | Aquariums, domestic water testing |
| Aquadur Nitrate Test Strips | Nitrate (NO3) | 0 – 100 ppm | Aquariums, agriculture, drinking water testing |
Performing the Aquadur Test: Aquadur Test Strips How To Read
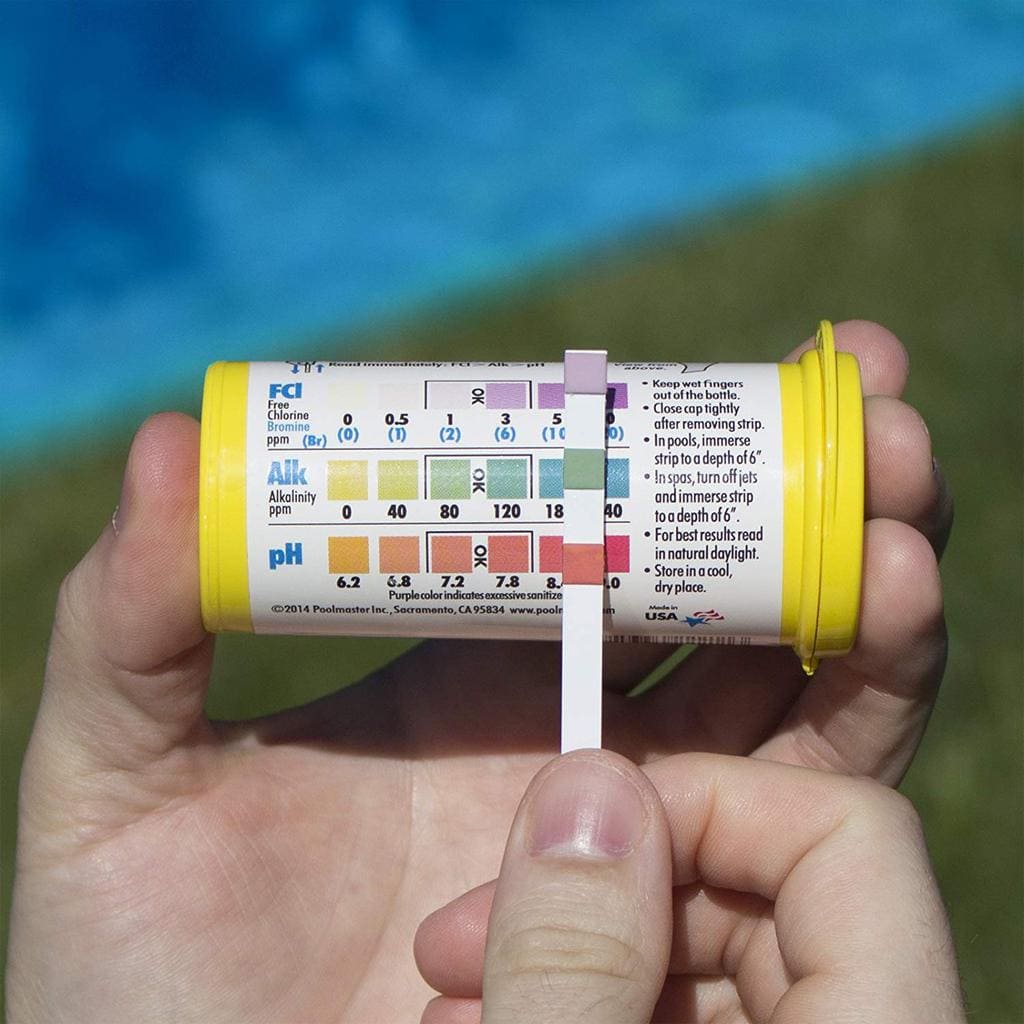
Accurately performing the Aquadur test is crucial for obtaining reliable water quality readings. Proper sample collection and adherence to the testing procedure are essential to minimize errors and ensure the results reflect the actual water conditions. This section details the steps involved in conducting a successful Aquadur test.
The Aquadur test involves using a test strip to measure various water parameters. The procedure requires careful attention to detail to avoid contamination and obtain accurate results. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions included with your specific Aquadur test strips, as variations may exist between different types of strips.
Sample Collection
Collecting a representative water sample is the first step in accurate testing. Avoid collecting water near the surface or from areas with visible sediment or debris. For tap water, allow the water to run for a few minutes before collecting the sample to flush out any stagnant water in the pipes. For other sources, such as a well or pond, collect the sample from the middle of the water body at a depth that represents the overall water quality.
The container used for sample collection should be clean and free of any contaminants that could affect the test results. Use a clean, dry container made of inert material that won’t leach chemicals into the water.
Performing the Test, Aquadur test strips how to read
Once you have collected a suitable sample, carefully remove an Aquadur test strip from its container. Avoid touching the reagent areas of the strip, as this can contaminate the test and lead to inaccurate results. Completely immerse the reagent area of the strip into the water sample for the time specified in the manufacturer’s instructions; this is typically a few seconds.
Remove the strip and gently shake off any excess water. Then, lay the strip flat on a clean, dry surface and allow the color to develop fully within the timeframe indicated on the packaging.
Avoiding Contamination
Contamination can significantly affect the accuracy of Aquadur test results. Avoid touching the reagent areas of the test strips. Ensure the container used for sample collection is clean and free of any substances that could interfere with the test. Perform the test in a clean area, away from any dust or other potential contaminants. If you accidentally touch the reagent area of the strip, discard it and use a new one.
Best Practices for Accurate Results
Several best practices can enhance the accuracy of Aquadur tests. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Use a fresh test strip for each test. Ensure the water sample is well-mixed before testing, particularly if the water is from a stagnant source. Compare the developed color on the test strip to the color chart provided on the container under good lighting conditions.
Note the time of day when performing the test, as some water parameters can fluctuate throughout the day.
Visual Guide to Using Aquadur Test Strips
This text-based guide illustrates the correct technique:
1. Gather Supplies
Clean container for sample, Aquadur test strip, and a clean, dry surface.
2. Collect Sample
Obtain a representative water sample, avoiding surface water or areas with debris.
Understanding Aquadur test strip readings involves comparing the strip’s color to the provided chart. Accurate measurements are crucial, and sometimes the strip’s dimensions, such as the length of the reactive area, might be relevant for comparison; for instance, if the reactive area is 144 mm long, you might need to know that this is equivalent to 144 mm is how many inches for precise analysis.
Therefore, referencing the provided conversion helps ensure accurate interpretation of Aquadur test strip results.
3. Prepare Strip
Remove a strip from the container, avoiding touching the reagent pads.
4. Immerse Strip
Fully submerge the reagent area in the sample for the specified time (e.g., 2 seconds).
5. Remove and Shake
Remove the strip and gently shake off excess water.
6. Compare to Chart
Lay the strip flat and compare the developed color to the color chart within the specified timeframe.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Inaccurate Aquadur test strip readings can stem from various sources, hindering accurate water quality assessment. Understanding these potential issues and implementing appropriate troubleshooting steps is crucial for reliable results. This section details common problems, their causes, and solutions, emphasizing the importance of proper technique and fresh test strips.
Several factors can contribute to inaccurate or unexpected results when using Aquadur test strips. These include issues with the test strips themselves, improper sample collection and handling, and environmental influences. Addressing these factors systematically is key to obtaining reliable water quality data.
Inaccurate Color Readings
Discrepancies between the test strip color and the color chart can arise from several factors. Improper timing during the testing process, where the color development is not allowed to complete fully, can lead to inaccurate readings. Additionally, insufficient mixing of the sample with the reactive area of the strip can result in uneven color development and inaccurate readings.
Finally, poor lighting conditions can affect color perception, leading to misinterpretation of the color chart. To ensure accuracy, follow the instructions carefully, ensuring adequate mixing and appropriate lighting conditions. Compare the developed color to the color chart under good lighting. If still unsure, repeat the test with a fresh strip and a new sample.
Unexpected Color Changes
Unexpected color changes beyond the range of the color chart can indicate contamination of the test strip, the sample, or both. Exposure of the test strips to moisture or extreme temperatures prior to use can alter their reactivity and lead to unreliable results. Similarly, if the water sample itself contains interfering substances, such as high concentrations of certain chemicals or particulate matter, it may affect the chemical reaction on the strip and lead to unusual color changes.
Always use fresh test strips stored according to manufacturer’s instructions and ensure the sample is representative of the water being tested, free from obvious contaminants.
Importance of Fresh Test Strips and Proper Sample Collection
Using expired or improperly stored test strips is a significant source of error. Exposure to moisture or extreme temperatures can degrade the reactive chemicals on the strips, leading to inaccurate readings or no color change at all. Similarly, improper sample collection techniques can introduce contaminants or affect the concentration of the measured parameter, leading to inaccurate results. For example, if testing for chlorine, collecting the sample in a container that has previously held chlorinated water will lead to artificially high readings.
Always use fresh test strips within their expiration date and store them according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure that the sample container is clean and free from any contaminants that might interfere with the test. Collect the sample directly from the source, avoiding splashing or contamination.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
The following flowchart Artikels a systematic approach to troubleshooting inaccurate Aquadur test strip readings:
Start -> Check expiration date of test strips -> (Yes: Discard strips and use fresh ones) -> (No: Proceed) -> Ensure proper sample collection technique -> (Yes: Proceed) -> (No: Recollect sample) -> Ensure proper mixing of sample and strip -> (Yes: Proceed) -> (No: Repeat with proper mixing) -> Check lighting conditions -> (Yes: Proceed) -> (No: Repeat in good lighting) -> Compare color to chart -> (Reading matches chart: End) -> (Reading doesn’t match chart: Repeat test with fresh strip and new sample) -> End
Array
Safe handling of Aquadur test strips is crucial to prevent potential health risks and ensure accurate results. The chemicals within the strips, while generally considered low-risk at the concentrations used, still require careful handling to minimize exposure. Proper disposal procedures are also essential to protect the environment.The chemicals present in Aquadur test strips are typically indicator dyes and binding agents.
While generally non-toxic at the levels used in the strips, direct contact with eyes or ingestion should be avoided. Skin contact may cause irritation in sensitive individuals. Inhalation of dust from broken or damaged strips should also be avoided. The specific chemical composition will vary depending on the manufacturer and type of Aquadur strip; always refer to the manufacturer’s Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for detailed information on the specific chemicals and associated hazards.
Potential Hazards and Chemical Handling
Aquadur test strips contain chemicals that, while generally safe for intended use, can pose risks if mishandled. These risks are primarily related to skin irritation, eye irritation, and potential allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Avoid direct contact with skin and eyes. In the event of skin contact, wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and water. If the chemical comes into contact with eyes, immediately flush with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
Ingestion should be treated as a medical emergency, requiring immediate medical attention. Always ensure adequate ventilation when handling multiple strips or in confined spaces to minimize inhalation of any potential dust particles.
Proper Disposal of Used Aquadur Test Strips
Used Aquadur test strips should be disposed of responsibly to prevent environmental contamination. Do not flush them down the toilet or dispose of them in regular household trash. Check with your local waste management authority for specific instructions on the disposal of chemical waste. In many cases, used test strips can be disposed of with regular household trash, but it’s crucial to confirm this with your local guidelines.
Always follow the manufacturer’s disposal recommendations provided on the product packaging or SDS. If large quantities of strips are used, consider contacting a hazardous waste disposal service.
Safety Measures
The following safety measures should always be followed when using Aquadur test strips:
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, when handling the test strips.
- Avoid direct contact with skin and eyes. Wash hands thoroughly after use.
- Handle the test strips carefully to avoid breakage and the release of any dust or chemicals.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to minimize inhalation of any potential dust.
- Store the test strips in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat.
- Keep test strips out of reach of children and pets.
- Dispose of used test strips according to local regulations and manufacturer recommendations.
- Refer to the manufacturer’s Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for detailed information on chemical hazards and safety precautions.
Mastering the use of Aquadur test strips empowers users to efficiently and accurately assess water quality. By following the Artikeld procedures for sample collection, testing, and result interpretation, alongside understanding and implementing the troubleshooting steps and safety precautions, users can confidently obtain reliable data for various applications. Remember to always consult the manufacturer’s instructions provided with your specific Aquadur test strips for detailed information and specific guidance.
Consistent application of these techniques ensures the reliable and safe use of these valuable tools for water quality analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I do if the color on the test strip doesn’t match the chart?
Ensure the strip was properly immersed and the correct immersion time was observed. Check the expiration date of the strips. If the problem persists, use a new batch of strips and repeat the test. If issues continue, contact the manufacturer.
How long are Aquadur test strips good for?
Check the expiration date printed on the container. Expired strips may provide inaccurate readings.
Can I reuse Aquadur test strips?
No, Aquadur test strips are for single use only. Reusing them will lead to inaccurate results.
Where can I buy replacement Aquadur test strips?
Check with your local pool supply store or online retailers that sell water testing supplies. The manufacturer’s website may also list authorized distributors.
