Black spots on teeth how to remove home remedies: This article explores various at-home methods for addressing unsightly black spots on teeth. We’ll examine the causes of these discolorations, ranging from minor surface stains to more serious underlying issues. Understanding the root cause is crucial before attempting any remedy, as some spots may require professional dental intervention.
We’ll delve into the efficacy and potential risks of popular home remedies, providing detailed instructions and precautions to ensure safe and effective application. Remember, while home remedies can offer improvement, professional dental care is essential for comprehensive treatment and diagnosis.
This guide will cover several popular home remedies, including baking soda and hydrogen peroxide, oil pulling, apple cider vinegar, and strawberry paste. Each remedy will be analyzed for its effectiveness, potential side effects, and appropriate application methods. We will also highlight the importance of considering individual oral health conditions and consulting a dentist before embarking on any at-home treatment plan.
Ultimately, the goal is to provide readers with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions about managing black spots on their teeth.
Introduction to Black Spots on Teeth
Black spots on teeth are a common dental concern, ranging from minor aesthetic issues to indicators of significant dental problems. Their appearance can vary greatly, and understanding the underlying causes is crucial for appropriate treatment and prevention. Ignoring black spots can lead to more extensive damage and potentially irreversible consequences.Black spots arise from various factors, primarily involving tooth decay (caries), staining, or underlying medical conditions.
The color, size, and location of the spot often provide clues to its origin. Prompt identification and professional evaluation are essential for effective management.
Types of Black Spots and Their Origins
Several factors contribute to the development of black spots on teeth. These factors often interact, making accurate diagnosis important. For example, a pre-existing cavity might become discolored due to food staining or bacterial byproducts.
- Dental Caries (Cavities): These are the most common cause of black spots. Bacteria produce acids that erode tooth enamel, creating holes that darken over time due to trapped food particles and bacterial pigments. These spots often appear rough or pitted to the touch.
- Staining: External staining from certain foods and beverages (like coffee, tea, red wine), tobacco use, or poor oral hygiene can lead to black or dark brown discoloration. These stains typically affect the outer enamel layer and are often more superficial than decay.
- Dental Fluorosis: Excessive fluoride intake during tooth development can cause discoloration, ranging from white spots to brown or black stains. The severity depends on the amount and duration of fluoride exposure.
- Medications: Certain medications, especially those containing tetracycline antibiotics, can cause tooth discoloration during tooth development, leading to black or gray spots. This is a developmental issue and not a result of later staining or decay.
- Trauma: Physical injury to a tooth can cause internal discoloration, resulting in a black spot. This is often accompanied by other symptoms, such as pain or sensitivity.
Significance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection of black spots is vital for preventing further damage and preserving tooth structure. Small cavities, for instance, are often treatable with minimal intervention, such as fluoride treatments or fillings. However, untreated cavities can progress, leading to more extensive damage, potentially requiring root canals or tooth extraction. Similarly, addressing staining early can prevent it from worsening and improve cosmetic appearance.
Addressing black spots on teeth often involves home remedies like oil pulling or baking soda paste. However, the effectiveness of these methods depends on the cause of the discoloration. Understanding the underlying issue can be insightful, much like exploring how others perceive you, as explained in this insightful article on 3 of swords how someone sees you.
Returning to teeth, consistent oral hygiene remains paramount in preventing future staining and maintaining a healthy smile.
In the case of fluorosis or medication-induced discoloration, early identification allows for appropriate management and preventive measures. A dental professional can accurately diagnose the cause of the black spot and recommend the most suitable treatment plan. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for early detection and prevention.
Home Remedies for Black Spots Removal
Black spots on teeth, also known as dental staining, can be caused by various factors including food and drinks (coffee, tea, red wine), tobacco use, poor oral hygiene, and certain medications. While professional cleaning is often the most effective solution, several home remedies may help lighten these discolorations. It’s crucial to remember that these remedies are not a substitute for regular dental checkups and professional cleaning.
Their effectiveness varies depending on the cause and severity of the staining.
Effectiveness and Limitations of Home Remedies for Black Spots
The success of home remedies for removing black spots on teeth depends heavily on the type and cause of the discoloration. Surface stains caused by food and drinks are often more responsive to home treatments than deeper stains caused by medications or intrinsic factors (discoloration originating within the tooth). It’s important to manage expectations; home remedies may offer minor improvements in some cases, but they may not completely eliminate stubborn or deep-seated stains.
Moreover, aggressive or improper use of home remedies can potentially damage tooth enamel.
Common Home Remedies for Black Spots on Teeth
Several home remedies have been suggested for teeth whitening, though scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness is often limited or inconclusive. It’s advisable to consult a dentist before trying any home remedy, particularly if you have sensitive teeth or existing dental issues.
| Remedy | Description | Application Method | Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baking Soda | A mild abrasive that can help scrub away surface stains. | Mix a small amount of baking soda with water to form a paste. Gently brush your teeth with the paste, then rinse thoroughly. Do not use more than once or twice a week. | Can be abrasive and damage enamel with overuse. Avoid if you have sensitive teeth. |
| Hydrogen Peroxide | A bleaching agent that can lighten stains. | Dilute 3% hydrogen peroxide with an equal amount of water. Rinse your mouth with the solution for a minute or two, then rinse with plain water. Do not swallow. Use sparingly, no more than once a day. | Can irritate gums and damage enamel with overuse or high concentrations. Not suitable for individuals with gum disease. |
| Oil Pulling | Involves swishing oil (typically coconut or sesame) in the mouth to remove bacteria and potentially improve oral health. | Swish 1-2 tablespoons of oil in your mouth for 15-20 minutes, then spit it out and rinse your mouth thoroughly. | May not directly whiten teeth but can improve oral hygiene, indirectly contributing to brighter teeth. Unscientific claims of significant whitening exist. |
| Strawberries | Contain malic acid, a natural bleaching agent. | Mash a strawberry and gently rub it on your teeth for a few minutes. Rinse thoroughly. | Limited evidence supports effectiveness. Acidic nature can erode enamel with frequent use. |
| Apple Cider Vinegar | Contains acetic acid, which may have some whitening properties. | Dilute apple cider vinegar with water (equal parts). Rinse your mouth with the solution for a minute or two, then rinse with plain water. Do not swallow. Use sparingly. | Highly acidic; frequent use can significantly damage tooth enamel and cause sensitivity. |
Comparison of Home Remedies
Baking soda and hydrogen peroxide are the most commonly used home remedies for teeth whitening. Baking soda’s abrasive action primarily targets surface stains, while hydrogen peroxide’s bleaching effect addresses both surface and some subsurface stains. However, both can damage enamel with overuse. Oil pulling and the use of strawberries or apple cider vinegar offer less conclusive evidence of effectiveness and carry the risk of enamel erosion due to their acidic nature.
The efficacy and safety of these methods are significantly lower compared to professional whitening treatments.
Baking Soda and Hydrogen Peroxide
Baking soda and hydrogen peroxide are commonly used home remedies for teeth whitening, purportedly capable of lightening surface stains and improving the overall appearance of teeth. However, it’s crucial to understand their mechanisms of action and potential risks before attempting this method.Baking soda’s abrasive nature helps to gently scrub away surface stains, while hydrogen peroxide’s bleaching properties work to lighten the tooth enamel.
Hydrogen peroxide releases oxygen molecules that break down chromogens, the colored molecules responsible for staining teeth. The combination of these two agents theoretically provides both a mechanical and chemical approach to stain removal.
Mechanism of Action
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) acts as a mild abrasive, physically removing surface stains from the teeth. Its slightly alkaline nature can also help neutralize acids produced by bacteria in the mouth, indirectly contributing to better oral hygiene. Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) is a bleaching agent that works by oxidizing the chromogens embedded in the tooth enamel. This oxidation process lightens the color of these stains, resulting in whiter-appearing teeth.
The combined effect of the abrasive action of baking soda and the bleaching action of hydrogen peroxide is believed to be more effective than using either substance alone.
Procedure for Using Baking Soda and Hydrogen Peroxide
A paste should be created by mixing a small amount of baking soda with a few drops of hydrogen peroxide to form a consistency similar to toothpaste. This paste should then be gently applied to the teeth using a soft-bristled toothbrush. Brush gently for one to two minutes, focusing on the stained areas. Thoroughly rinse the mouth with water afterward.
This procedure should ideally be performed once or twice a week, as more frequent use may increase the risk of enamel erosion.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While generally considered safe when used sparingly, the combined use of baking soda and hydrogen peroxide carries potential risks. Baking soda’s abrasive nature, if used excessively or with vigorous brushing, can lead to enamel erosion over time, increasing the teeth’s sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures. Hydrogen peroxide, a bleaching agent, can also irritate the gums and soft tissues of the mouth if not used carefully.
Excessive use can also lead to tooth sensitivity and potential damage to the enamel. Individuals with sensitive teeth or existing gum problems should avoid this method. Additionally, it is important to note that this method may not be effective for all types of stains, particularly deep-seated intrinsic stains.
Precautions
Always use a soft-bristled toothbrush to minimize enamel abrasion. Avoid vigorous brushing. Limit application to once or twice a week. Rinse thoroughly after application to remove any residue. If you experience any irritation, sensitivity, or discomfort, discontinue use immediately and consult a dentist.
This home remedy is not a substitute for professional teeth whitening procedures. For significant or persistent discoloration, it is recommended to seek the advice of a dental professional. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the most suitable treatment option.
Oil Pulling
Oil pulling is an ancient Ayurvedic practice involving swishing oil in the mouth for several minutes to improve oral health. Proponents claim it removes bacteria, reduces inflammation, and whitens teeth, potentially contributing to the removal of black spots. However, scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited and often inconclusive.Oil pulling typically involves using a tablespoon of oil, such as coconut, sesame, or sunflower oil, swished around the mouth for 10-20 minutes.
The oil is then spat out, and the mouth is rinsed with water. The process is believed to draw out toxins and bacteria from the mouth, leading to improved oral hygiene. The purported benefits extend beyond teeth whitening to include reduced plaque, gingivitis, and bad breath.
Scientific Evidence Regarding Oil Pulling’s Effectiveness for Black Spot Removal
While anecdotal evidence abounds, rigorous scientific studies investigating oil pulling’s effectiveness in removing black spots from teeth are scarce. Existing research primarily focuses on its impact on general oral health markers like plaque and gingivitis. These studies often show a modest reduction in these parameters, but the direct link to black spot removal remains unproven. More research with larger sample sizes and standardized methodologies is needed to definitively establish oil pulling’s efficacy in this specific area.
The mechanisms by which oil pulling might affect black spots are also unclear and require further investigation. For example, it’s unclear whether the mechanical action of swishing oil is sufficient to dislodge deeply embedded stains or whether other factors, such as antimicrobial properties of the oil, are at play.
Comparison of Oil Pulling with Other Home Remedies, Black spots on teeth how to remove home remedies
Compared to other home remedies like baking soda and hydrogen peroxide, oil pulling offers a gentler approach. Baking soda and hydrogen peroxide, while effective in some cases, can be abrasive and potentially damage tooth enamel with prolonged or frequent use. Oil pulling, on the other hand, is generally considered less abrasive. However, its effectiveness in removing black spots is significantly less supported by scientific evidence than the bleaching effects of hydrogen peroxide.
The convenience factor also differs; oil pulling requires a longer time commitment compared to the relatively quick application of baking soda paste or hydrogen peroxide rinse. Furthermore, the taste and texture of oil pulling might be less appealing to some individuals compared to the other methods. The cost effectiveness is comparable across these methods, with all three options being relatively inexpensive.
Apple Cider Vinegar: Black Spots On Teeth How To Remove Home Remedies

Apple cider vinegar (ACV) has gained popularity as a purported teeth whitening agent. Its acidity, however, presents a potential risk to dental health. While some anecdotal evidence suggests benefits, scientific backing is limited, and caution is advised. Understanding ACV’s properties and potential effects on tooth enamel is crucial before considering its use for teeth whitening.Apple cider vinegar’s acidity, primarily due to acetic acid, can erode tooth enamel.
Enamel, the hard outer layer of teeth, protects against decay and sensitivity. The low pH of ACV (typically around 2.5 to 3.5) can weaken enamel over time, making teeth more susceptible to cavities and sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures. This erosive effect is not immediate but can accumulate with repeated exposure. The degree of damage depends on factors like the concentration of the vinegar, frequency of use, and individual oral health.
Safe Use of Apple Cider Vinegar for Teeth Whitening
Using apple cider vinegar for teeth whitening requires extreme caution and should only be attempted with proper dilution and limited frequency. Undiluted ACV should never be applied directly to teeth. The following guidelines are crucial for minimizing the risk of enamel damage:
- Always dilute ACV: Mix one tablespoon of ACV with one cup of water. This significantly reduces the acidity and minimizes the risk of enamel erosion.
- Rinse, don’t swish: Briefly rinse your mouth with the diluted solution for no more than 60 seconds. Avoid prolonged contact with teeth.
- Limit frequency: Use the diluted ACV rinse no more than once or twice a week at most. Overuse significantly increases the risk of enamel damage.
- Neutralize with water: After rinsing with the diluted ACV, thoroughly rinse your mouth with plain water to neutralize the acid.
- Follow with fluoride toothpaste: Use a fluoride toothpaste after rinsing to help remineralize the enamel and protect against further damage.
Risks Associated with Overuse of Apple Cider Vinegar on Teeth
Overuse or improper use of apple cider vinegar for teeth whitening can lead to several detrimental effects on dental health. These risks include:
- Enamel erosion: This is the most significant risk. Repeated exposure to the acid weakens the enamel, leading to increased sensitivity, discoloration, and a higher susceptibility to cavities.
- Tooth sensitivity: As the enamel erodes, the underlying dentin becomes exposed, making teeth more sensitive to temperature changes, sweet foods, and acidic drinks.
- Increased risk of cavities: Weakened enamel provides less protection against bacteria and acids that cause cavities.
- Discoloration: While ACV might initially appear to whiten teeth, the long-term effects of enamel erosion can actually lead to discoloration and staining.
- Gum irritation: The acidity of ACV can irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and discomfort.
Strawberry Paste
Strawberries have gained popularity as a potential teeth-whitening agent due to their naturally occurring compounds. While not a substitute for professional dental cleaning, the application of strawberry paste is sometimes touted as a home remedy for removing superficial stains. The effectiveness, however, varies significantly depending on the type and severity of discoloration.The primary active component believed to contribute to strawberry’s whitening effect is malic acid.
Malic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) that possesses mild abrasive properties. It can help to gently remove surface stains from teeth. Strawberries also contain various antioxidants, which may contribute to overall oral health, although their direct impact on teeth whitening is less well-established.
Strawberry Paste Application Method
Creating and applying a strawberry paste involves a simple process. First, thoroughly mash one fresh, ripe strawberry to create a smooth paste. Ensure there are no seeds remaining that could scratch the enamel. Then, gently apply the paste directly to the teeth using a soft-bristled toothbrush. Allow the paste to remain on the teeth for approximately five minutes before rinsing thoroughly with lukewarm water.
It is crucial to avoid swallowing the paste. This process can be repeated once or twice a week, but overuse is strongly discouraged.
Limitations and Potential Drawbacks of Strawberry Paste
While the mild abrasiveness of malic acid might offer some superficial stain removal, the effects of strawberry paste are generally temporary and limited. It is not effective against deep-seated stains or discoloration caused by underlying dental issues. Moreover, the acidic nature of strawberries can potentially erode tooth enamel with repeated or prolonged use. This erosion can lead to increased sensitivity and a higher risk of cavities.
The abrasive nature of the seeds, if not removed completely, could also contribute to enamel wear. Therefore, it’s essential to use this remedy sparingly and with caution. For significant teeth discoloration or any concerns about oral health, consulting a dentist is always recommended. They can provide professional assessment and treatment options tailored to individual needs.
Visual Aids
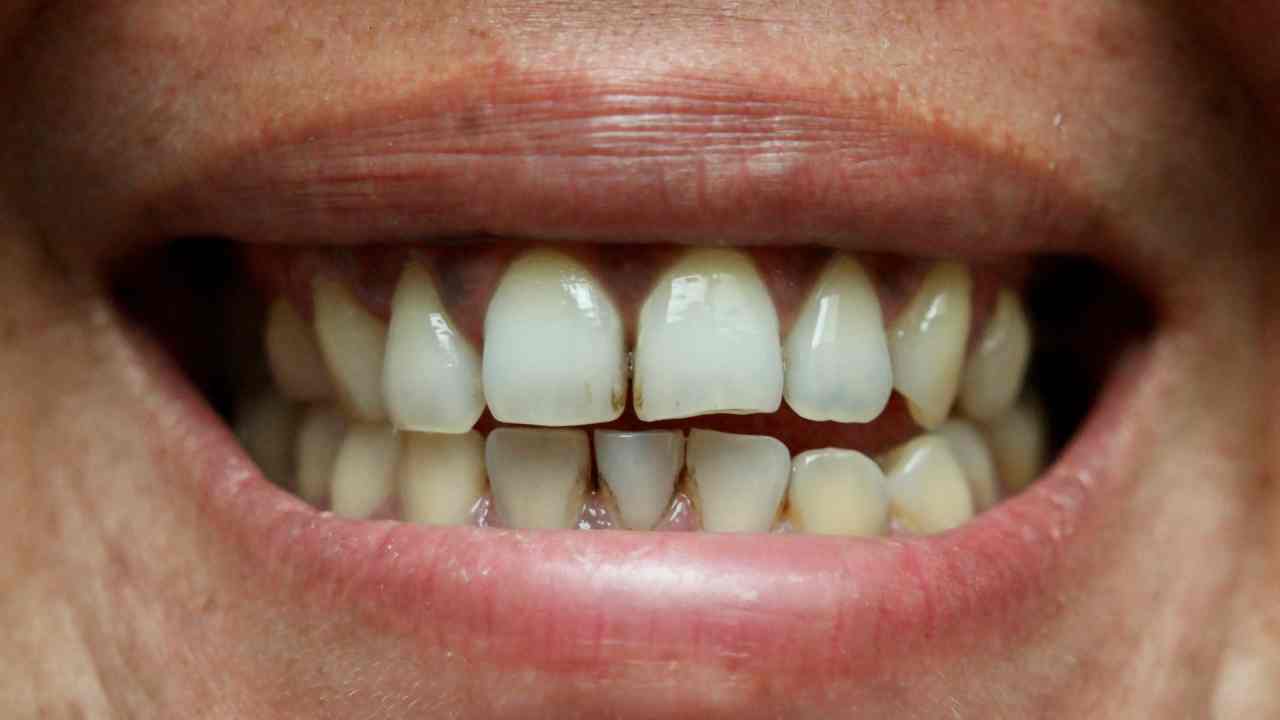
Before-and-after photographs are a valuable tool for illustrating the potential effectiveness of home remedies for black spots on teeth. These visual comparisons can demonstrate changes in tooth color, texture, and overall appearance, providing a clearer understanding of the treatment’s impact. However, it is crucial to remember that individual results may vary depending on the severity of the discoloration, the chosen remedy, and the individual’s oral hygiene practices.The effectiveness of home remedies is often limited, and significant improvements might not always be visible.
Dramatic changes shown in some before-and-after images may be due to factors other than the treatment alone, including improved oral hygiene, professional cleaning, or even the natural variation in tooth color over time. Therefore, these images should be interpreted cautiously, and it’s essential to manage expectations realistically.
Before and After Image Descriptions
A typical before image might show teeth with noticeable black spots, varying in size and intensity. The spots could appear dull and pitted against a background of generally yellowish or off-white enamel. The overall texture of the teeth may appear uneven, with the areas around the black spots potentially showing some degree of surface roughness. The color contrast between the black spots and the surrounding enamel is often stark, making the discoloration highly visible.
The image may also reveal other imperfections such as minor staining or minor plaque buildup.In contrast, the after image, following a course of home remedies, might show a slight reduction in the size or intensity of the black spots. The color of the affected areas may be somewhat lighter, appearing less dark and more integrated with the surrounding enamel.
While complete removal might not be achieved, the overall appearance of the teeth might appear brighter and cleaner. The texture might appear smoother, although significant changes in texture are less likely with home remedies. The contrast between the treated areas and the rest of the tooth surface will be less pronounced. It’s important to note that any improvement will be subtle and gradual; significant changes typically require professional intervention.
Array
While home remedies can sometimes offer mild aesthetic improvements for superficial black spots on teeth, it’s crucial to understand their limitations and potential risks. These methods are not substitutes for professional dental care and should not be relied upon for significant or persistent discoloration. Over-reliance on home remedies may delay appropriate treatment, potentially worsening the underlying dental issue.The effectiveness of home remedies varies greatly depending on the cause and severity of the black spots.
Factors such as the type of stain, the depth of discoloration, and the individual’s oral hygiene practices all play a significant role in determining the outcome. Furthermore, some home remedies, if used improperly or excessively, can damage tooth enamel or irritate the gums.
Situations Requiring Professional Dental Intervention
It is important to seek professional dental care for black spots on teeth in several circumstances. Ignoring these situations could lead to more serious dental problems.
- Persistent or worsening discoloration: If the black spots do not improve or worsen despite home remedies, a dentist should be consulted to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
- Pain or sensitivity: Any pain, sensitivity to hot or cold, or discomfort associated with the black spots necessitates immediate professional evaluation. This could indicate tooth decay, an abscess, or other dental problems.
- Large or deep spots: Extensive discoloration that covers a significant portion of the tooth or appears deep within the tooth structure requires professional assessment and treatment.
- Suspected decay or cavities: If the black spot is accompanied by other signs of decay, such as a hole in the tooth or a rough texture, immediate professional intervention is crucial to prevent further damage.
- Bleeding gums: Bleeding gums alongside black spots may indicate gum disease (gingivitis or periodontitis), which needs prompt professional treatment.
- Underlying medical conditions: Certain medical conditions can contribute to tooth discoloration. A dentist can help identify any underlying health issues that may be contributing to the problem.
- Significant aesthetic concerns: While home remedies may offer minor improvements, individuals with significant aesthetic concerns regarding tooth discoloration should consult a dentist for professional whitening or cosmetic procedures.
Addressing black spots on teeth effectively requires a balanced approach combining informed self-care with professional dental guidance. While home remedies can offer supplemental support in improving the appearance of minor discolorations, they are not a replacement for regular dental checkups and professional cleaning. Remember that the underlying cause of the black spots needs to be addressed, and severe cases or persistent discoloration warrant immediate consultation with a dentist.
This guide offers a starting point for understanding the options available, but professional advice remains crucial for achieving optimal oral health and a confident smile.
Expert Answers
What causes black spots on teeth?
Black spots can result from various factors including tooth decay (cavities), trauma, excessive fluoride intake, certain medications, or poor oral hygiene.
Are home remedies always effective for black spots?
The effectiveness of home remedies varies depending on the cause and severity of the discoloration. Minor surface stains may respond well, while deeper discolorations often require professional treatment.
How often should I use home remedies for teeth whitening?
Frequency depends on the specific remedy and its potential for enamel erosion. Follow the instructions carefully and avoid overuse to prevent damage to your teeth.
When should I see a dentist about black spots on my teeth?
Consult a dentist if black spots are accompanied by pain, sensitivity, or if home remedies don’t improve the discoloration. Professional evaluation is crucial to rule out serious underlying conditions.
