Aquadur test strips how to read – Aquadur test strips: how to read them accurately is crucial for obtaining reliable results. These strips provide a quick and convenient method for various water quality assessments, from testing pool chemicals to analyzing water samples in research settings. Understanding the different types of Aquadur strips, their proper usage, and result interpretation is essential for ensuring accurate readings and informed decision-making.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the entire process, from sample collection to interpreting the color changes and troubleshooting potential issues.
Aquadur test strips come in various formulations, each designed for specific parameters. Understanding the intended use of each type is paramount. Proper storage, as detailed in this guide, ensures the strips maintain their accuracy and reliability. The testing procedure itself involves careful sample collection and precise immersion of the strip, followed by a comparison of the resulting color change to the manufacturer’s color chart.
This guide will clarify the significance of each color change and help identify potential sources of error.
Understanding Aquadur Test Strips
Aquadur test strips are rapid diagnostic tools used to assess the quality of water by detecting specific parameters. Their ease of use and portability make them valuable for various applications, from monitoring water purity in aquariums to field testing during environmental assessments. Understanding their functionality and limitations is crucial for accurate interpretation of results.Aquadur test strips function through a colorimetric reaction.
The strips contain chemical reagents that react with specific substances in the water sample, producing a color change. The intensity of the color change corresponds to the concentration of the substance being measured. This allows for a quick, visual assessment of water quality without the need for specialized laboratory equipment.
Types of Aquadur Test Strips and Their Uses
Different Aquadur test strips are designed to measure various water parameters. These parameters often include pH, chlorine, alkalinity, and hardness. Each strip type contains a specific reagent combination tailored to the parameter it measures. For example, a pH test strip will measure the acidity or alkalinity of the water, while a chlorine test strip will measure the concentration of free chlorine.
The choice of strip depends entirely on the specific water quality parameters that need to be assessed. Some advanced strips may even combine multiple tests on a single strip for comprehensive analysis.
Proper Storage of Aquadur Test Strips
Maintaining the accuracy of Aquadur test strips requires careful storage. Improper storage can lead to degradation of the reagents, resulting in inaccurate readings. The strips should always be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. The original container should be tightly sealed to prevent exposure to air and humidity. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for specific storage recommendations as these may vary depending on the type of strip.
Expired strips should be discarded and replaced with new ones.
Accuracy and Sensitivity Comparison of Aquadur Test Strip Models
The accuracy and sensitivity of Aquadur test strips vary depending on the model and the parameter being measured. Generally, higher-priced models tend to offer greater accuracy and sensitivity. However, even the most sensitive strips have limitations and should not be considered a replacement for laboratory-grade analysis for precise measurements. The following table provides a general comparison (note that specific values may vary based on manufacturer and batch):
| Model | Parameter | Accuracy | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aquadur Basic | pH (6.5-8.5) | ±0.2 pH units | 0.5 pH units |
| Aquadur Pro | pH (4.0-10.0), Chlorine | ±0.1 pH units, ±0.2 ppm Cl | 0.25 pH units, 0.1 ppm Cl |
| Aquadur Advanced | pH (4.0-10.0), Chlorine, Alkalinity | ±0.1 pH units, ±0.1 ppm Cl, ±5 ppm Alk | 0.2 pH units, 0.05 ppm Cl, 2 ppm Alk |
| Aquadur Premium | pH (4.0-10.0), Chlorine, Alkalinity, Hardness | ±0.05 pH units, ±0.05 ppm Cl, ±2 ppm Alk, ±10 ppm Hardness | 0.1 pH units, 0.025 ppm Cl, 1 ppm Alk, 5 ppm Hardness |
Note: ppm refers to parts per million; Alk refers to alkalinity; These values are illustrative and may not reflect the exact specifications of all Aquadur test strip models. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for the most accurate information.
The Testing Procedure
Accurate use of Aquadur test strips is crucial for obtaining reliable water quality readings. The following steps Artikel the proper procedure, emphasizing the importance of meticulous adherence to the manufacturer’s instructions. Deviations from the prescribed method can lead to inaccurate results and misinterpretations of water quality.The testing procedure involves several key steps: sample collection, strip immersion, and result interpretation.
Each step requires careful attention to detail to ensure the validity of the test. Following the manufacturer’s instructions precisely is paramount for obtaining accurate and reliable results.
Sample Collection
Proper sample collection is the foundation of accurate testing. The water sample should be representative of the water body being tested. Avoid collecting samples near the surface where contaminants may be concentrated or from areas with obvious sources of contamination. For example, when testing a well, avoid collecting water immediately after pumping. Allow the water to flow for a few minutes before collecting the sample.
The sample container should be clean and free of any substances that could contaminate the water. It is recommended to use a clean, sterile container to avoid introducing any foreign substances into the sample.
Strip Immersion and Reaction Time
Once a representative sample has been collected, carefully remove an Aquadur test strip from its container. Avoid touching the reagent pads with your fingers to prevent contamination. Completely immerse the reagent pads in the water sample for the specified duration as indicated on the test strip packaging. Do not submerge the strip beyond the indicated line. This ensures consistent exposure of the reagent pads to the water sample, leading to reliable readings.
After immersion, remove the strip and gently blot the edge on a clean, absorbent surface to remove excess water.
Timing and Result Interpretation
Precise timing is essential. After removing the strip from the water sample, carefully observe the color changes on the reagent pads. Compare the colors to the color chart provided on the packaging. Note the exact time elapsed after removing the strip from the sample. Compare the color of each reagent pad to the corresponding color chart within the specified timeframe provided by the manufacturer.
Any deviation from the recommended timing can affect the accuracy of the test results. For example, if the manufacturer recommends reading the results after 60 seconds, waiting longer or shorter will likely lead to an inaccurate reading.
Best Practices for Accurate Results
Several best practices enhance the accuracy and reliability of Aquadur test strip results. Always ensure the test strips are stored properly in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture, to maintain the integrity of the reagents. Before each test, visually inspect the strips for any signs of damage or degradation. Discard any damaged or expired strips.
Additionally, it is recommended to perform multiple tests using different strips from the same batch to verify consistency. This helps to minimize the risk of errors and provides a more reliable assessment of water quality.
Flowchart of the Testing Process
A flowchart visually represents the complete testing process:[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with “Collect Water Sample,” branching to “Ensure Clean Container and Representative Sample.” This would lead to “Remove Test Strip,” branching to “Avoid Touching Reagent Pads.” Next would be “Immerse Strip Completely for Specified Time,” branching to “Remove and Blot Excess Water.” Finally, “Compare to Color Chart and Record Results” would be the terminal node.]
Interpreting Results
Accurate interpretation of Aquadur test strip color changes is crucial for understanding water quality. The strips are designed to react with specific water parameters, producing a color change that corresponds to a measurable value. Comparing the strip’s color to the color chart provided is essential for obtaining reliable results.The color change on the Aquadur test strip reflects the concentration of the substance being measured.
A more intense color generally indicates a higher concentration, while a lighter color or no change suggests a lower concentration. However, it is critical to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and compare the test strip to the chart under the correct lighting conditions to avoid misinterpretations. The accuracy of the reading is dependent on proper technique and adherence to the specified testing procedure.
Color Chart Interpretation
The Aquadur test strip’s color chart provides a visual guide for interpreting the results. Each color shade corresponds to a specific measurement range. For example, a deep blue might indicate a high chlorine level, while a pale blue might represent a low chlorine level. It is important to note that the color gradations on the chart are often subtle, requiring careful comparison.
The chart should be examined under consistent lighting to ensure accurate reading.
Factors Influencing Test Results
Several factors can influence the accuracy of Aquadur test strip results. These include the water temperature, the presence of interfering substances in the water sample, and the time elapsed between dipping the strip and comparing it to the color chart. High water temperatures can accelerate the reaction, potentially leading to inaccurate readings. Similarly, the presence of other chemicals or minerals in the water sample might interfere with the color reaction.
The manufacturer’s instructions will specify the optimal testing conditions and time limits for accurate results. For example, a cloudy water sample may obscure the true color change, making it difficult to get an accurate reading. Similarly, allowing too much time to elapse before comparing the strip to the chart can lead to color fading or further reactions, affecting the accuracy.
Visual Guide to Color Changes
The following bullet points illustrate examples of color changes and their corresponding interpretations. Remember that these are examples and the specific color shades may vary slightly depending on the Aquadur test strip version and the specific parameter being measured. Always refer to the color chart included with your specific Aquadur test strips.* Chlorine: A deep blue color might indicate a chlorine level of 5 ppm, while a light blue might indicate 1 ppm.
A colorless strip suggests a very low or absent chlorine level.
pH
A dark red color might indicate a pH of 7.5, a green color might suggest a neutral pH of 7.0, and a dark blue might indicate a pH of 6.5. These values are illustrative and the exact color and numerical correlation will vary based on the specific Aquadur test strip.
Understanding Aquadur test strips involves recognizing the color changes indicated on the strip’s scale. Interpreting these results can be complex, much like understanding how someone perceives you, a concept explored in depth by examining the symbolism of the Tarot card, 2 of pentacles as how someone sees you. This card’s duality mirrors the nuanced readings sometimes required with Aquadur strips; precise color matching is key to accurate interpretation.
Therefore, careful comparison to the provided chart is crucial for obtaining reliable results from Aquadur testing.
Total Hardness
A dark purple might suggest high hardness, a light purple medium hardness, and a pale purple or colorless might indicate low hardness. Again, the specific color-to-measurement relationship should be verified with the included chart.
Troubleshooting Common Issues: Aquadur Test Strips How To Read
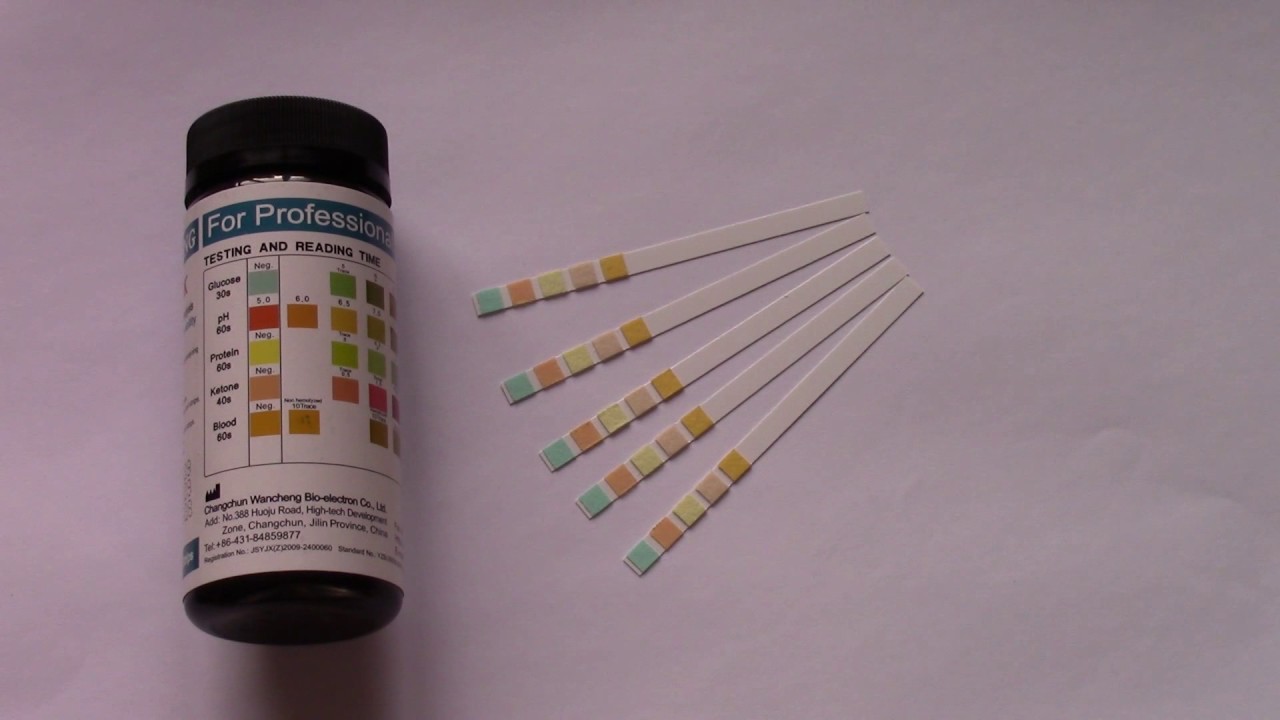

Aquadur test strips, while generally reliable, can sometimes produce unclear or inconsistent results. Understanding potential sources of error and implementing appropriate troubleshooting steps is crucial for obtaining accurate water quality assessments. This section details common problems and their solutions to ensure accurate interpretation of your test results.
Unclear or Faint Color Change
Several factors can lead to unclear or faint color changes on the Aquadur test strips. These include insufficient immersion time, using contaminated water samples, or using expired test strips. To address these issues, ensure the strip is fully submerged in the water sample for the specified duration, use a clean, representative sample of the water, and always check the expiration date on the test strip container before testing.
If the problem persists after these steps, consider using a new batch of test strips to rule out expired or damaged strips as the cause.
Inconsistent Results Between Tests
Variations in test results can stem from several sources. Improper sample collection techniques, inconsistent immersion time, or variations in water temperature can all influence the final reading. To minimize inconsistencies, consistently collect samples from the same location and depth, strictly adhere to the recommended immersion time, and ensure the water temperature remains relatively consistent between tests. If inconsistencies persist after careful attention to these factors, a new batch of test strips may be necessary to eliminate the possibility of a manufacturing defect in the original batch.
Color Mismatch with the Color Chart
Discrepancies between the test strip color and the provided color chart can be due to lighting conditions, observer bias, or degradation of the test strip itself. Always compare the test strip to the color chart under consistent, good lighting conditions. Avoid comparing the strip under direct sunlight or in low light environments. Multiple individuals can independently compare the color to minimize subjective interpretation.
If significant discrepancies remain after these steps, it may be indicative of a problem with the test strips themselves, and a new batch should be used.
Contamination of Test Strips, Aquadur test strips how to read
Improper handling can lead to contamination of the test strips, resulting in inaccurate readings. Avoid touching the reagent areas of the strips, ensure the test strip container is properly closed after each use, and store the strips in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. If contamination is suspected, discard the affected strips and use a fresh batch.
Improper Sample Collection
Using an unrepresentative water sample can lead to inaccurate readings. Ensure the sample is collected from the appropriate location and depth, and that it is well-mixed before testing. For stagnant water bodies, gently stir the water before collecting the sample to ensure a homogeneous sample is tested. For flowing water, collect the sample downstream of any potential sources of contamination.
Safety Precautions and Considerations
Safe and proper handling of Aquadur test strips is crucial to ensure accurate results and prevent potential hazards. This section details necessary precautions, potential risks, and safe disposal methods. Ignoring these precautions may compromise the accuracy of the test and potentially expose the user to risks.Proper handling of Aquadur test strips and samples minimizes the risk of inaccurate readings and potential health hazards.
The strips themselves contain chemical reagents that, while generally safe when used as directed, can cause irritation if mishandled. Similarly, the samples being tested may contain contaminants that require careful handling.
Handling Test Strips and Samples
Avoid touching the reagent pads on the test strips. Handle the strips only by the edges to prevent contamination. Always use clean, dry hands when handling both the test strips and the samples. If using gloves, ensure they are clean and appropriate for the sample type. Store unused test strips in their original container, away from moisture and extreme temperatures, to maintain their integrity and accuracy.
Samples should be collected and handled in a manner consistent with the safety precautions associated with their source. For example, samples taken from potentially contaminated water sources should be handled with extra care to prevent exposure to pathogens.
Potential Hazards of Improper Use
Improper use or handling of Aquadur test strips can lead to several hazards. Contamination of the reagent pads can produce inaccurate or unreliable test results. Exposure of the reagent pads to excessive moisture or heat can degrade the reagents, leading to incorrect readings. Ingestion of the reagents could cause mild irritation of the mouth and digestive tract.
Skin contact with the reagents may cause mild skin irritation in sensitive individuals. Improper disposal of used test strips can lead to environmental contamination.
Safe Disposal of Used Test Strips
Used Aquadur test strips should be disposed of according to local regulations. In most cases, they can be treated as regular household waste, but it’s advisable to check with local authorities for specific guidelines. Never flush the used test strips down the toilet or dispose of them in a way that could contaminate the environment. Dispose of the strips in a sealed, appropriately labeled container to avoid accidental contact.
Health Risks Associated with Incorrect Interpretation
Incorrect interpretation of Aquadur test results can have significant health consequences. For example, a false negative result indicating safe water when it is actually contaminated could lead to waterborne illness. Conversely, a false positive result might lead to unnecessary anxiety and potentially the rejection of safe drinking water. It is imperative to carefully follow the instructions for interpreting results and, if uncertain, to seek further professional advice or testing.
Always consult with a healthcare professional or relevant authority if you have concerns about the safety of your water supply.
Final Conclusion
Mastering the use of Aquadur test strips empowers users with a valuable tool for water quality analysis. By following the step-by-step procedures Artikeld in this guide, users can confidently obtain accurate and reliable results. Remember, careful attention to detail throughout the process—from proper storage and sample collection to accurate color interpretation—is key to avoiding errors and ensuring the integrity of the test results.
Regularly reviewing this guide and consulting the manufacturer’s instructions will help maintain proficiency and accuracy in using Aquadur test strips.
FAQ Insights
What should I do if the color change on the strip is unclear?
Repeat the test with a fresh strip and a new sample. Ensure proper lighting and compare the color to the chart under similar lighting conditions. If the issue persists, contact the manufacturer.
How long are Aquadur test strips good for?
The expiration date is printed on the packaging. Do not use expired strips.
Can I reuse Aquadur test strips?
No, Aquadur test strips are for single use only. Using a used strip will lead to inaccurate results.
What are the potential health risks associated with handling Aquadur test strips?
Avoid direct contact with eyes and skin. Wash hands thoroughly after use. Refer to the manufacturer’s safety data sheet for detailed information.
