Black spots on teeth how to remove home remedies – Black spots on teeth: how to remove them with home remedies? This question plagues many, prompting a search for safe and effective solutions. Understanding the underlying causes of these discolorations—whether extrinsic (surface stains) or intrinsic (internal stains)—is crucial for selecting the appropriate approach. This guide explores various home remedies, their effectiveness, potential risks, and when professional dental intervention becomes necessary.
We’ll delve into the science behind natural whitening agents and emphasize the importance of consistent oral hygiene practices to prevent future discoloration.
We will examine several common causes of black spots, including tooth decay, trauma, and medication side effects. Visual differences between these causes will be highlighted, along with the role of medical history in diagnosis. A detailed comparison of home remedies like baking soda, oil pulling, and hydrogen peroxide will be presented, focusing on their efficacy and safety profiles.
Additionally, we’ll explore natural alternatives such as strawberries and activated charcoal, explaining their mechanisms of action. Finally, we’ll Artikel when professional intervention, such as teeth whitening or bonding, is the most appropriate course of action.
Introduction to Black Spots on Teeth: Black Spots On Teeth How To Remove Home Remedies
Black spots on teeth are a common dental concern, ranging from mild cosmetic blemishes to indicators of more serious underlying issues. Understanding the causes of these discolorations is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. The appearance of black spots can significantly impact a person’s self-confidence and oral health.Black spots on teeth result from a variety of factors, broadly categorized as extrinsic or intrinsic staining.
Addressing black spots on teeth often involves home remedies like oil pulling or baking soda paste. However, understanding how others perceive your smile, perhaps even influenced by these imperfections, is also important. For insights into how someone might view your outward presentation, consider exploring the tarot card meaning of the Six of Wands, as explained in this helpful article: 6 of wands how someone sees you.
Ultimately, consistent oral hygiene practices, alongside addressing any underlying causes of discoloration, remain crucial for achieving a healthy and confident smile.
Extrinsic stains affect the outer layer of the tooth, the enamel, while intrinsic stains penetrate deeper into the dentin, the underlying layer of the tooth. Both types can lead to noticeable discoloration, but their causes and treatment options differ significantly.
Causes of Black Spots on Teeth
Several factors contribute to the development of black spots on teeth. These include external factors like diet and lifestyle choices, as well as internal factors related to tooth development and underlying medical conditions. Understanding these contributing factors allows for targeted preventative measures and appropriate treatment strategies.
- Dietary Factors: Consumption of highly pigmented foods and beverages such as coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored berries can lead to extrinsic staining, resulting in surface discoloration that may appear as black spots. The tannins and chromogens in these substances bind to the enamel, causing discoloration over time.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking and chewing tobacco are significant contributors to both extrinsic and intrinsic staining. Nicotine and tar in tobacco products stain the enamel, leading to yellowing and browning, and can also penetrate the dentin, causing deeper, more persistent discoloration.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque and bacteria to accumulate on the teeth. This buildup can lead to discoloration, including the formation of black spots, particularly in areas where plaque is most likely to accumulate, such as along the gum line.
- Dental Caries (Cavities): Untreated cavities can lead to the discoloration of the affected tooth. As the decay progresses, the tooth may darken, eventually appearing as a black spot. This darkening is often accompanied by other symptoms such as toothache and sensitivity to hot and cold.
- Medications: Certain medications, particularly those containing tetracycline antibiotics, can cause intrinsic staining during tooth development in children and young adults. This staining can result in black or gray discoloration that is permanent and requires professional treatment.
- Trauma: Injury to a tooth can lead to internal bleeding and discoloration, resulting in a black spot. This type of staining is usually intrinsic and may require restorative treatment such as a dental crown or filling.
Extrinsic versus Intrinsic Staining
The distinction between extrinsic and intrinsic staining is crucial for determining appropriate treatment. Extrinsic stains are superficial and often easier to remove, while intrinsic stains require more extensive intervention.Extrinsic stains reside on the enamel surface and are primarily caused by external factors like food, drinks, and tobacco. These stains can often be removed through professional cleaning or home remedies like whitening toothpastes.Intrinsic stains, however, are embedded within the dentin and are typically caused by internal factors like medications or trauma.
These stains are more challenging to remove and may require professional treatments such as bleaching or veneers.
Overview of Home Remedies for Teeth Discoloration
Several home remedies can help address mild extrinsic staining, improving the appearance of black spots. However, it’s important to note that these remedies are not effective for all types of discoloration, and professional dental care is often necessary for significant or intrinsic staining. The effectiveness of home remedies also varies depending on the severity and cause of the discoloration.
- Baking Soda: Baking soda is a mild abrasive that can help remove surface stains. It should be used cautiously and sparingly, as excessive use can damage enamel.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Hydrogen peroxide has bleaching properties and can lighten surface stains. It should be diluted with water and used cautiously to avoid irritation.
- Oil Pulling: This involves swishing oil (such as coconut or sesame oil) in the mouth for several minutes. Some believe this helps remove plaque and improve the appearance of teeth, but scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness is limited.
- Strawberry Paste: Strawberries contain malic acid, which some believe has mild whitening properties. However, like baking soda, it should be used cautiously due to its abrasiveness.
Identifying the Cause of Black Spots
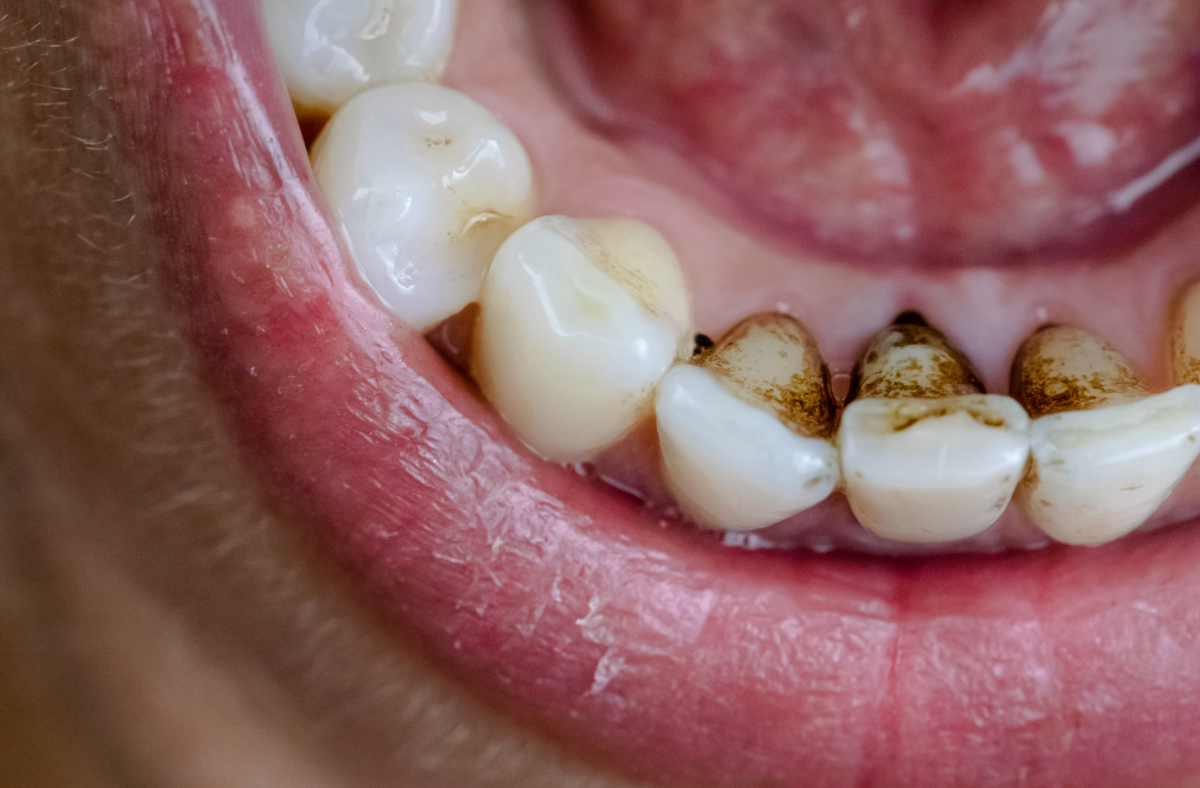
Black spots on teeth can stem from various sources, each exhibiting distinct visual characteristics. Accurate identification requires careful observation of the spot’s appearance and consideration of the individual’s medical history. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective or even harmful treatment, highlighting the importance of professional dental evaluation.Black spots are not always indicative of a serious problem; however, prompt identification of the underlying cause is crucial for appropriate management.
The size, shape, location, and texture of the spot, along with the patient’s history of dental trauma, medication use, and overall health, provide crucial clues for diagnosis.
Visual Characteristics of Black Spots from Different Sources
The appearance of a black spot can vary significantly depending on its origin. Decay, for example, often presents as a progressively enlarging, dark brown or black area that may be rough or pitted to the touch. This discoloration results from the breakdown of tooth enamel and dentin by bacteria. In contrast, black spots caused by trauma might appear as a sharply defined, localized area of discoloration, often associated with a history of injury to the tooth.
Medication-induced discoloration may present as a diffuse, generalized darkening of the tooth surface, rather than a localized spot.
The Role of Medical History in Identifying the Cause
A thorough medical history is essential in determining the cause of black spots. For instance, a patient’s history of tetracycline use during tooth development can indicate tetracycline staining, which manifests as a yellowish-brown or grayish-black discoloration, particularly affecting the molars. Similarly, a history of fluorosis (excessive fluoride intake) may result in mottled discoloration, ranging from white flecks to brown or black spots.
A history of trauma, such as a blow to the mouth, is crucial in considering trauma-induced discoloration. The presence of other systemic diseases or conditions can also influence the development of black spots on teeth, further emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive medical evaluation.
Comparing and Contrasting the Appearance of Black Spots, Black spots on teeth how to remove home remedies
The following table summarizes the visual characteristics of black spots from different causes:
| Cause | Appearance | Additional Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Dental Decay (Caries) | Dark brown or black, often pitted or rough texture, may be accompanied by sensitivity to temperature changes. | Progressive enlargement, localized to a specific area of the tooth. |
| Trauma | Sharply defined, localized black or dark brown discoloration. | Often associated with a history of injury, may be accompanied by pain or sensitivity. |
| Tetracycline Staining | Yellowish-brown or grayish-black discoloration, often affecting multiple teeth. | Usually affects teeth that developed during tetracycline use. |
| Fluorosis | Mottled discoloration, ranging from white flecks to brown or black spots. | Severity depends on the level of fluoride exposure during tooth development. |
| Amalgam Tattoo | Bluish-black discoloration, usually located near the gum line. | Associated with dental fillings containing mercury amalgam. |
Home Remedies for Black Spots Removal
Several home remedies are purported to lighten or remove black spots on teeth. However, it’s crucial to understand that their effectiveness varies greatly depending on the cause of the discoloration and individual responses. While some may offer mild improvements, they are not a substitute for professional dental treatment, especially for significant discoloration or underlying dental issues. Always consult a dentist before attempting any home remedies, particularly if you have sensitive teeth or existing dental conditions.
Comparison of Home Remedies for Black Spot Removal
The following table compares the effectiveness and safety of common home remedies for black spots on teeth. Note that the effectiveness is subjective and results may vary.
| Remedy | Effectiveness | Safety | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baking Soda Paste | Mildly abrasive, may remove surface stains; effectiveness varies depending on stain type and severity. | Generally safe when used sparingly and correctly; can cause enamel erosion with overuse. | Use a low concentration and avoid frequent use. |
| Oil Pulling | Limited scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness for teeth whitening; may improve oral hygiene. | Generally safe; may cause nausea or allergic reactions in some individuals. | Use food-grade oils and avoid swallowing the oil. |
| Hydrogen Peroxide | Can bleach teeth, but may cause sensitivity and gum irritation; effectiveness varies. | Can be harmful if swallowed; can irritate gums and teeth with prolonged use. | Use a low concentration and avoid prolonged contact with teeth and gums. |
Baking Soda Paste Application
A baking soda paste can be prepared by mixing a small amount of baking soda with a few drops of water to form a paste. This paste should be applied gently to the teeth using a soft-bristled toothbrush. Brush gently for one to two minutes, then rinse thoroughly with water. It’s crucial to avoid excessive brushing or pressure, as this can damage enamel.
This method should be used infrequently, perhaps once or twice a week at most, to minimize the risk of enamel erosion. For significant stains, this remedy is unlikely to be effective.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Home Remedies
Overuse or improper application of these home remedies can lead to several adverse effects. Baking soda’s abrasiveness can erode tooth enamel over time, leading to increased sensitivity and potential damage. Hydrogen peroxide, while a bleaching agent, can irritate gums and cause tooth sensitivity if used excessively or at high concentrations. Oil pulling, while generally safe, may trigger allergic reactions in some individuals or cause nausea if swallowed.
It’s important to remember that these remedies address only superficial stains and will not be effective against stains caused by underlying dental problems. Persistent or worsening discoloration warrants a visit to a dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Natural Whitening Agents
Several natural substances possess mild bleaching properties that may help lighten surface stains on teeth. However, it’s crucial to understand that these methods are not as effective as professional whitening treatments and may not address all types of discoloration. Furthermore, overuse can potentially damage tooth enamel. Always consult a dentist before attempting any home whitening remedies.The effectiveness of these natural agents is often debated, and results can vary significantly depending on the type and severity of staining, as well as individual oral hygiene practices.
These methods should be considered complementary to, not a replacement for, regular dental checkups and professional cleaning.
Strawberry Whitening
Strawberries contain malic acid, a naturally occurring alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA). AHAs are known for their exfoliating properties, which can help remove surface stains from teeth.
- Preparation: Mash a fresh strawberry to create a paste.
- Application: Gently rub the strawberry paste onto your teeth for about 5 minutes. Rinse thoroughly with water afterward.
- Frequency: Use this method no more than once or twice a week to avoid enamel erosion.
Apple Cider Vinegar Whitening
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) contains acetic acid, another mild acid that can help remove surface stains. However, its acidic nature makes it crucial to use it sparingly to prevent enamel damage.
- Preparation: Dilute apple cider vinegar with an equal amount of water.
- Application: Dip a soft-bristled toothbrush into the diluted solution and gently brush your teeth for 1-2 minutes. Rinse thoroughly with water afterward.
- Frequency: Use this method no more than once a week.
Activated Charcoal Whitening
Activated charcoal, a highly porous material, is believed to absorb surface stains on teeth. However, its abrasive nature requires careful application to avoid enamel damage. The effectiveness of activated charcoal for teeth whitening is not definitively proven and requires further research.
- Preparation: Purchase food-grade activated charcoal powder.
- Application: Dip a wet toothbrush into the powder and gently brush your teeth for 1-2 minutes. Rinse thoroughly and completely with water afterward.
- Frequency: Use this method sparingly, no more than once or twice a week.
Oral Hygiene Practices for Preventing Black Spots
Maintaining optimal oral hygiene is crucial in preventing the formation of black spots on teeth. Consistent and thorough cleaning removes surface stains and plaque buildup, minimizing the risk of discoloration and decay. Effective brushing and flossing techniques, combined with the use of appropriate oral hygiene products and regular professional cleanings, form the cornerstone of a preventative strategy.Proper brushing involves using a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle, circular motions.
Imagine moving the brush head in small circles, covering each tooth surface thoroughly – the outer, inner, and chewing surfaces. Pay particular attention to the gum line, where plaque often accumulates. Brush for at least two minutes, twice a day, ensuring that you reach all areas of your mouth. For the back molars, use a back-and-forth motion to effectively clean these harder-to-reach areas.
Replacing your toothbrush every three to four months, or sooner if the bristles become frayed, is also important to maintain brushing effectiveness.
Recommended Toothpaste and Mouthwash for Stain Prevention
Choosing toothpastes and mouthwashes with stain-removing properties can complement your brushing and flossing routine. Many commercially available toothpastes contain mild abrasives that help remove surface stains without damaging tooth enamel. Look for toothpastes that specifically advertise stain removal or whitening properties. Similarly, some mouthwashes contain ingredients that can help reduce plaque and bacteria, contributing to overall oral health and stain prevention.
Examples of ingredients to look for in both toothpastes and mouthwashes include fluoride (for strengthening enamel) and antimicrobial agents to fight bacteria. However, always consult with a dentist or hygienist before using any new oral hygiene product, particularly if you have sensitive teeth or existing dental conditions.
Importance of Regular Dental Checkups and Professional Cleanings
Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings are essential components of preventative oral care. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup that home care alone may not eliminate. Tartar, a hardened form of plaque, can contribute significantly to stain formation and gum disease. During these cleanings, a dental hygienist uses specialized tools to thoroughly clean your teeth and remove stains.
Regular checkups allow dentists to detect any potential problems early on, such as cavities or gum disease, which can also contribute to discoloration. The frequency of professional cleanings is typically recommended every six months, though this may vary depending on individual needs and risk factors. Early detection and treatment of oral health issues can help prevent more serious problems, including the development of black spots and other forms of tooth discoloration.
When to Seek Professional Help

While many minor black spots on teeth might respond to home remedies, certain situations necessitate professional dental intervention. Ignoring persistent or worsening discoloration can lead to more significant dental problems, impacting both aesthetics and oral health. Professional treatment offers more effective and long-lasting solutions compared to home remedies, particularly for severe cases or specific types of discoloration.Professional dental care is crucial when home remedies fail to show improvement after a reasonable period, typically several weeks of consistent application.
This is particularly true if the black spots are accompanied by pain, sensitivity, or other symptoms suggesting underlying dental issues such as decay or gum disease. Furthermore, the size, location, and nature of the discoloration can influence the decision to seek professional help. Large, deep, or rapidly spreading black spots often require professional assessment and treatment.
Professional Treatments for Black Spots
Several professional treatments effectively address black spots on teeth, each with its own advantages, disadvantages, and cost implications. The choice of treatment depends on the cause and severity of the discoloration, as well as the patient’s individual preferences and budget.
- Teeth Whitening: This procedure uses bleaching agents to lighten the overall tooth color, potentially reducing the visibility of superficial black spots. In-office whitening provides faster results than at-home kits, but it’s generally more expensive. The effectiveness of whitening varies depending on the type and cause of the discoloration; it’s less effective for intrinsic stains (those originating within the tooth structure) and may not address deep or extensive black spots.
The cost can range from a few hundred to over a thousand dollars depending on the method and location.
- Dental Bonding: This cosmetic procedure involves applying a tooth-colored resin to the affected area, masking the black spot. Bonding is a relatively inexpensive and quick procedure, suitable for small, superficial spots. However, it’s less durable than other options and may require replacement over time. The resin can also chip or stain. The cost typically ranges from $100 to $500 per tooth.
- Veneers: Veneers are thin, custom-made shells that cover the front surface of the teeth. They effectively mask discoloration and can improve the overall appearance of the teeth. Veneers are more expensive than bonding and whitening, but they offer a more durable and natural-looking solution. They are a good option for multiple or large black spots. The cost typically ranges from $800 to $2000 per tooth.
Cost and Benefit Comparison of Professional Treatments
The cost of professional treatments varies significantly, influencing the choice of procedure. Teeth whitening is generally the most affordable option, but its effectiveness is limited by the type and severity of discoloration. Dental bonding is a relatively inexpensive alternative for small, superficial spots, while veneers represent a more substantial investment but provide a long-lasting and aesthetically pleasing solution. The benefits should be weighed against the costs and individual circumstances.
For instance, a single small black spot might be effectively treated with bonding, whereas numerous or large spots might necessitate veneers for a comprehensive solution. A thorough consultation with a dentist is essential to determine the most appropriate and cost-effective treatment plan.
Illustrative Examples of Black Spot Causes and Treatments
Understanding the varied causes of black spots on teeth is crucial for effective treatment. The appearance of a black spot can vary depending on its underlying cause, ranging from a small, barely noticeable discoloration to a larger, more prominent stain. The following examples illustrate different scenarios and their respective treatments.
Case Studies of Black Spots on Teeth
This section presents three distinct cases demonstrating the diverse causes and treatments for black spots on teeth. Each case highlights the importance of accurate diagnosis for effective management.
Case 1: Dental Caries (Cavity)
This case involves a 35-year-old patient presenting with a dark brown to black spot on the occlusal (chewing) surface of a posterior molar. The spot was accompanied by sensitivity to temperature changes and mild discomfort when chewing. A clinical examination and radiograph confirmed a deep carious lesion (cavity). Before treatment, the black spot was visibly noticeable, irregular in shape, and slightly raised above the surrounding tooth structure.
The patient did not attempt any home remedies. Professional treatment involved the removal of the decayed tooth structure using a dental drill, followed by the placement of a composite resin filling. After treatment, the black spot was completely eliminated, and the tooth surface appeared smooth and restored to its natural color. The restoration blended seamlessly with the adjacent tooth structure.
Case 2: Dental Fluorosis
A 12-year-old patient exhibited multiple small, white to brown-black spots scattered across the enamel of their anterior teeth (front teeth). This discoloration resulted from excessive fluoride intake during tooth development. The spots were generally flat and did not compromise the tooth structure’s integrity. No home remedies were attempted. In this case, the aesthetic concern was the primary issue.
Professional treatment focused on improving the appearance of the discoloration through microabrasion, a process that gently removes the surface layer of enamel to reduce the intensity of the spots. In addition, professional teeth whitening was considered to minimize the contrast between the affected and unaffected areas. After treatment, the spots were significantly less noticeable, and the overall appearance of the teeth was improved.
The teeth appeared brighter and more uniform in color.
Case 3: Extrinsic Staining from Beverages
A 28-year-old patient presented with a diffuse, dark brown-black staining on the anterior teeth. This discoloration was primarily attributed to the long-term consumption of coffee and tea without adequate oral hygiene. The staining was relatively superficial and did not affect the underlying tooth structure. The patient initially tried various home remedies, including brushing with baking soda and hydrogen peroxide, but experienced minimal improvement.
The black staining was widespread, affecting most of the visible surfaces of the front teeth. Professional treatment involved in-office teeth whitening using a high-concentration bleaching agent. After treatment, the black staining was significantly reduced, and the teeth appeared noticeably whiter. The overall improvement in the appearance was dramatic, with a significant reduction in the intensity of the discoloration.
| Case | Cause of Black Spots | Home Remedy Tried (if any) | Professional Treatment Used | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Dental Caries (Cavity) | None | Composite Resin Filling | Complete removal of black spot; tooth restored. |
| Case 2 | Dental Fluorosis | None | Microabrasion and Teeth Whitening | Significant reduction in spot visibility; improved aesthetics. |
| Case 3 | Extrinsic Staining (Coffee/Tea) | Baking soda and hydrogen peroxide | In-office Teeth Whitening | Significant reduction in staining; whiter teeth. |
Epilogue
Addressing black spots on teeth effectively requires a multi-pronged approach. While home remedies can be helpful for mild surface stains and preventative care, understanding their limitations is crucial. This guide has explored various options, emphasizing the importance of identifying the underlying cause of discoloration and practicing meticulous oral hygiene. Remember, consistent brushing, flossing, and regular dental checkups are paramount in preventing black spots and maintaining a healthy, bright smile.
When home remedies prove insufficient, seeking professional dental care is essential for effective and safe treatment.
Answers to Common Questions
Can I use lemon juice to whiten my teeth?
While lemon juice is acidic and might seem to lighten teeth initially, its high acidity can erode tooth enamel, increasing sensitivity and making teeth more susceptible to staining over time. Avoid using lemon juice for teeth whitening.
How often should I use baking soda for teeth whitening?
Use baking soda paste sparingly, no more than once or twice a week. Excessive use can damage enamel.
Are all black spots on teeth serious?
No. Some are merely surface stains, while others indicate underlying dental problems like decay. Professional evaluation is crucial to determine the cause.
What’s the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic staining?
Extrinsic stains are on the tooth’s surface (e.g., coffee stains). Intrinsic stains are within the tooth structure (e.g., from tetracycline medication).
