Aquadur test strips how to read – Aquadur test strips: how to read them accurately is crucial for obtaining reliable water quality assessments. These strips offer a convenient and relatively inexpensive method for determining various water parameters, from pH levels to the presence of specific contaminants. Understanding the proper techniques for using and interpreting Aquadur test strips is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of your water quality analysis.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the process, from sample collection to result interpretation, helping you to confidently utilize these valuable tools.
This guide covers the different types of Aquadur test strips, their applications, proper storage techniques, step-by-step testing procedures, detailed color chart interpretation, troubleshooting common issues, and essential safety precautions for handling and disposal. By following the instructions carefully, users can gain valuable insights into their water quality and take appropriate actions based on the test results.
Understanding Aquadur Test Strips
Aquadur test strips are designed for rapid, on-site water quality assessment. They provide a convenient and cost-effective method for determining various water parameters, crucial for various applications ranging from environmental monitoring to industrial process control. Understanding their functionality and proper usage is essential for obtaining reliable results.
Aquadur Test Strip Applications and Types
Aquadur test strips are used across a broad spectrum of applications. These include monitoring drinking water quality, analyzing water in swimming pools and spas, testing aquarium water, and assessing water quality in various industrial processes. The specific type of Aquadur test strip employed depends on the parameter(s) needing measurement. Common parameters include pH, chlorine, bromine, and total alkalinity.
Aquadur offers individual strips for single-parameter testing and multi-parameter strips for simultaneous measurements. For instance, a single-parameter strip might measure only chlorine levels, while a multi-parameter strip could simultaneously test for pH and chlorine. The choice depends on the specific needs of the user.
Aquadur Test Strip Storage for Accuracy
Proper storage is vital to maintaining the accuracy and reliability of Aquadur test strips. Exposure to moisture, extreme temperatures, and light can degrade the reagents embedded in the strips, leading to inaccurate readings. Aquadur test strips should always be stored in their original, tightly sealed container in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight. The optimal storage temperature is typically between 15°C and 25°C (59°F and 77°F).
Always check the expiration date on the container and discard any expired strips. Failure to adhere to these storage guidelines may compromise the integrity of the test results.
Comparison of Aquadur Test Strip Models
The following table compares some key features and specifications of different Aquadur test strip models. Note that the availability of specific models may vary depending on region and supplier.
| Model Name | Parameters Measured | Range | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aquadur pH Strip | pH | 6.8 – 8.2 | ±0.2 pH units |
| Aquadur Chlorine Strip | Free Chlorine | 0-10 ppm | ±0.5 ppm |
| Aquadur Combo Strip (Example) | pH, Chlorine, Total Alkalinity | pH: 6.8-8.2; Chlorine: 0-10 ppm; Alkalinity: 80-200 ppm | pH: ±0.2; Chlorine: ±0.5 ppm; Alkalinity: ±10 ppm |
| Aquadur Bromine Strip | Bromine | 0-10 ppm | ±0.5 ppm |
Performing the Aquadur Test
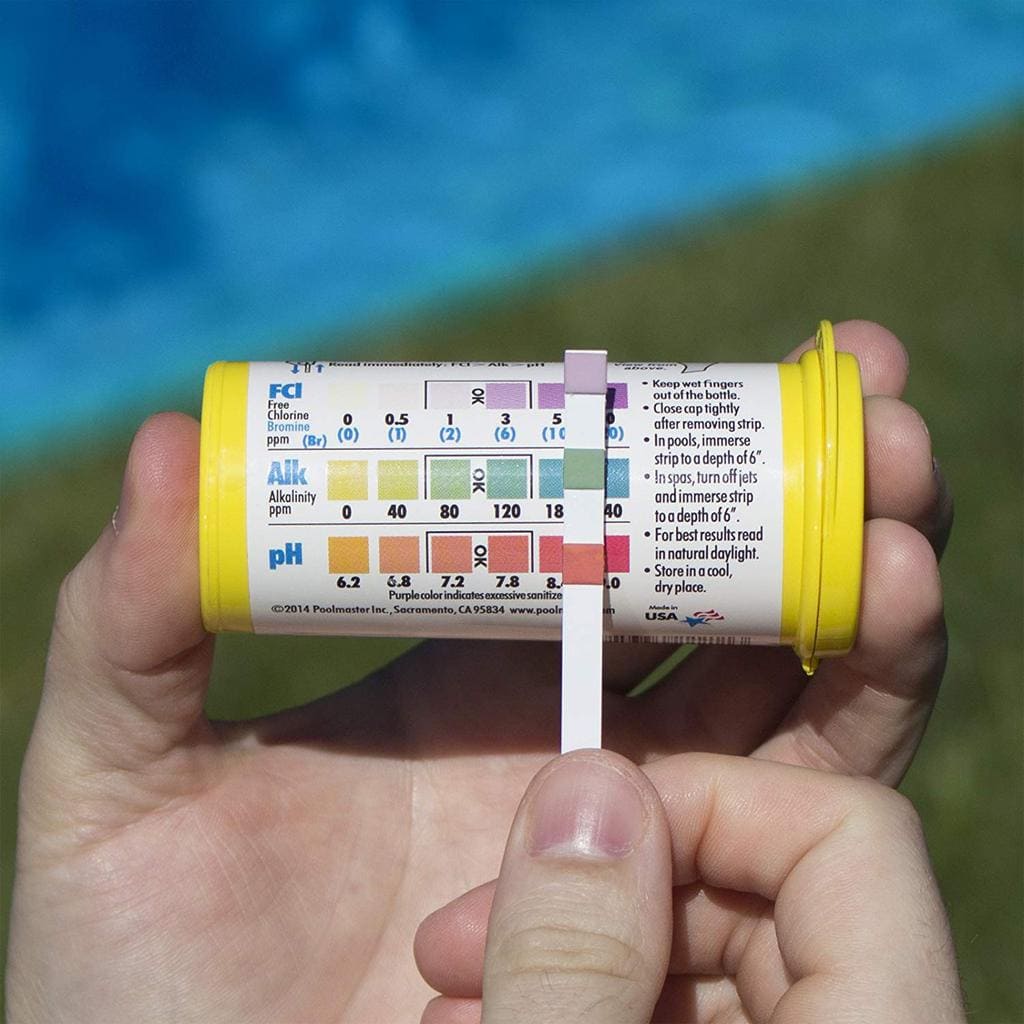
Accurate testing with Aquadur test strips requires careful sample collection and precise adherence to the manufacturer’s instructions. Following these procedures ensures reliable results and minimizes the risk of inaccurate readings.The process involves three key stages: sample collection, strip application, and color chart comparison. Each stage requires attention to detail to achieve accurate water quality assessment.
Sample Collection
Collecting a representative water sample is crucial for obtaining accurate test results. Avoid collecting water from areas with stagnant water or near sources of contamination. The sample should be collected from the main body of water, ensuring it represents the overall water quality. For example, if testing a swimming pool, the sample should be taken from the center of the pool, away from the walls and filtration system.
The container used for sample collection should be clean and free of any residues that could affect the test results. Ideally, use a clean, sterile container. Before collecting the sample, rinse the container with the water to be tested and discard the rinse water. This helps prevent contamination from the container itself. Ensure the container is filled to the appropriate level indicated on the test strip packaging or instructions.
Test Strip Application
Once a representative sample has been collected, carefully remove an Aquadur test strip from its container. Avoid touching the reagent pads on the strip to prevent contamination. Completely immerse the reagent pads in the water sample to the indicated line on the strip. The immersion time should precisely follow the manufacturer’s instructions, typically a few seconds. Remove the strip and gently blot the edge on a clean, absorbent paper towel to remove excess water.
Avoid blotting the reagent pads themselves. This blotting step helps to remove any excess water that might dilute the color reaction. This is important because excess water could lead to a less intense color development, potentially resulting in an inaccurate reading.
Color Chart Comparison
After the specified reaction time (usually indicated on the test strip packaging), compare the color of the reagent pads to the color chart provided. The color chart displays a range of colors corresponding to different water quality levels. Hold the test strip next to the color chart under good lighting conditions, preferably natural daylight. Avoid comparing the strip under dim lighting or fluorescent lights, which can distort color perception.
The color of the reagent pads should be matched to the closest color on the chart to determine the water quality parameter being tested (e.g., chlorine level, pH). If the color falls between two shades on the chart, choose the closest match or, if the uncertainty is significant, repeat the test with a fresh sample and a new test strip.
Interpreting Aquadur Test Strip Results: Aquadur Test Strips How To Read
Accurate interpretation of Aquadur test strip results is crucial for understanding your water quality. The color changes on the strip correspond to specific levels of various water quality parameters, as indicated on the accompanying color chart. Proper interpretation allows for informed decisions regarding water treatment or further testing.
Aquadur test strips typically measure multiple water quality parameters simultaneously. Each parameter will have its own designated area on the strip, displaying a distinct color change. The intensity of the color change, compared to the color chart provided with the strips, indicates the concentration of that specific parameter in the water sample. It’s essential to carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper test procedure and timing to ensure accurate results.
Color Changes and Corresponding Readings
The Aquadur test strip color chart displays a gradient of colors for each parameter tested. For example, a parameter like chlorine might show a range from pale yellow (low chlorine concentration) to dark yellow or orange (high chlorine concentration). Similarly, other parameters such as pH, alkalinity, or hardness will exhibit a unique color spectrum. Each color corresponds to a specific numerical value, enabling precise quantification of the parameter.
For instance, a specific shade of blue might indicate a pH of 7.0, while a deeper blue could represent a pH of 7.5. The chart’s legend provides a clear and detailed explanation of the color-to-value correspondence for each parameter.
Interpreting Results Using the Color Chart
To interpret the results, hold the test strip next to the color chart under good lighting. Compare the color developed in each test area of the strip to the color gradients on the chart. Find the closest matching color on the chart for each parameter. The numerical value associated with that color represents the concentration of the parameter in your water sample.
For instance, if the chlorine test area shows a color matching the “3 ppm” mark on the chart, then the chlorine concentration in your water sample is approximately 3 parts per million. Remember to consult the specific instructions and chart provided with your Aquadur test strips as color charts may vary slightly between different product batches.
Comparison of Different Readings and Their Implications
Different readings on the Aquadur test strip indicate varying water quality. For instance, a high chlorine reading might suggest chlorinated water, while a low reading might indicate insufficient disinfection. Similarly, a high pH reading may suggest alkaline water, potentially impacting the taste and corrosiveness, while a low pH could indicate acidic water, also posing potential issues. High levels of hardness minerals can lead to scale buildup in pipes and appliances, while low hardness might impact the taste and feel of the water.
By comparing your readings to the acceptable ranges specified by health authorities or your local water supplier, you can assess the suitability of your water for drinking and other uses. For example, a reading of total dissolved solids significantly higher than the recommended level may indicate the need for filtration. Conversely, readings within the acceptable range suggest good water quality.
Flowchart for Decision-Making Based on Aquadur Test Strip Results
A flowchart can simplify the interpretation and decision-making process based on Aquadur test strip results. The flowchart will visually guide users through the analysis, starting with comparing each parameter reading against the acceptable range. If all parameters are within the acceptable range, the flowchart concludes with “Water is suitable for intended use.” If any parameter falls outside the acceptable range, the flowchart directs the user to the appropriate course of action, such as further testing, water treatment, or contacting a water specialist.
The flowchart can incorporate conditional statements to cater to specific scenarios, such as high levels of a particular contaminant requiring a specialized treatment approach.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Accurate Aquadur test strip results depend on proper technique and handling. Several factors can influence the accuracy of the test, leading to unclear results or discrepancies. Understanding these potential sources of error and implementing corrective measures is crucial for reliable water quality assessment.
Errors can stem from various stages of the testing process, from sample collection to result interpretation. Improper sample collection, such as using a contaminated container or failing to thoroughly mix the sample, can introduce inaccuracies. Similarly, incorrect storage conditions, like exposure to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight, can degrade the sample and affect the test’s accuracy. Furthermore, failing to follow the manufacturer’s instructions precisely, such as dipping the strip to the correct depth or reading the results within the specified timeframe, can also lead to unreliable outcomes.
Finally, even subtle variations in the color comparison can cause misinterpretations if the user is not careful or experienced in reading the color chart.
Solutions for Unclear or Inconsistent Results
Addressing issues with unclear or inconsistent Aquadur test strip results requires a systematic approach. First, ensure the test strips are within their expiration date and have been stored correctly. A visual inspection of the strips before use is also important; discard any that show signs of damage or discoloration. If the results are unclear, repeat the test with a fresh sample, carefully following all instructions.
Pay close attention to the timing of the color development, ensuring the reading occurs within the specified time window. If inconsistencies persist, compare the results to a known standard solution of similar water quality to confirm the accuracy of the test strip. If the problem continues, consider contacting the manufacturer for technical support.
Frequently Asked Questions
Addressing common questions about Aquadur test strips and their interpretation is vital for accurate water quality assessment. The following points clarify several frequently raised concerns.
- What should I do if the color on the test strip doesn’t match any of the colors on the chart? This often indicates the water parameter is outside the range detectable by the test strip. You may need a different test strip with a wider measurement range or an alternative testing method for more precise results.
- How do I store Aquadur test strips properly? Store the test strips in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Keep the container tightly sealed to maintain the integrity of the strips.
- Can I reuse Aquadur test strips? No, Aquadur test strips are for single use only. Reusing them can lead to inaccurate and unreliable results.
- What if I accidentally touch the reagent pads on the test strip before testing? Avoid touching the reagent pads. If you do, use a new test strip for accurate results.
- My results seem inconsistent between tests. What could be causing this? Inconsistent results could be due to improper sample collection, incorrect storage of the strips or sample, or not following the instructions carefully. Ensure that you are following the instructions precisely and using fresh test strips and samples for each test.
Example of an Inaccurate Test and Correction, Aquadur test strips how to read
Imagine a scenario where a user tests a water sample and the Aquadur strip shows a color indicating high chlorine levels. However, the user knows from previous reliable testing methods that the chlorine level is typically low. This discrepancy suggests an error. To correct this, the user should first check the expiration date of the test strip and ensure proper storage.
They should then repeat the test using a new strip and a freshly collected, well-mixed sample, ensuring they follow the instructions precisely, including the correct immersion time and reading the results within the specified time frame. If the high chlorine reading persists, they should consider using a different testing method for verification, such as a more sophisticated laboratory test, to confirm the accuracy of the initial result.
If the repeated test using the correct procedures now shows a low chlorine level, the initial result is deemed inaccurate, likely due to improper technique or a faulty test strip.
Safety Precautions and Disposal
Safe handling and disposal of Aquadur test strips are crucial to prevent potential health risks and environmental contamination. Improper use can lead to exposure to chemicals and inaccurate test results. This section details the necessary precautions and proper disposal methods.Aquadur test strips, while generally safe for intended use, contain chemicals that may cause irritation or allergic reactions if mishandled.
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions provided with the product. Avoid direct contact with eyes and skin. If contact occurs, immediately flush the affected area with plenty of water and seek medical attention if necessary. The specific chemicals used in Aquadur test strips vary depending on the parameters being measured; refer to the product’s Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for detailed information on the composition and potential hazards.
Understanding Aquadur test strips involves comparing the color change to the provided chart. Accurate readings depend on proper immersion time; for example, if a specific parameter requires a 2-inch strip immersion, consider the actual length involved – referencing a guide like 2 inches how long can be helpful for visualizing the correct depth. Precise measurement ensures reliable results when interpreting Aquadur test strip color changes.
Handling Precautions
Always handle Aquadur test strips with clean, dry hands. Avoid touching the reagent pads on the strips, as this can contaminate the test and lead to inaccurate results. Work in a well-ventilated area to minimize exposure to any potential fumes. Never ingest the test strips or their components. Store the strips in their original container, away from direct sunlight, heat, and moisture, to maintain their integrity and accuracy.
Disposal Procedures
Used Aquadur test strips should be disposed of according to local regulations. In most cases, they can be treated as household hazardous waste. Never flush used test strips down the toilet or drain. Check with your local waste management authority for specific guidelines on the disposal of chemical waste in your area. If large quantities of test strips are being used, consult a hazardous waste disposal company for appropriate handling and disposal procedures.
Used containers should also be disposed of properly, following the same guidelines as the test strips themselves.
Health Risks Associated with Improper Handling or Disposal
Improper handling of Aquadur test strips may lead to skin or eye irritation, allergic reactions, or ingestion of harmful chemicals. Disposal of used strips in inappropriate ways, such as flushing them down the toilet or throwing them in regular trash, can contaminate water sources and harm the environment. Ingestion of the chemicals contained within the test strips can cause serious health problems, depending on the specific chemicals and the amount ingested.
Safe Storage Practices
To maintain the quality and accuracy of Aquadur test strips, proper storage is essential. Store them in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Keep the container tightly sealed to prevent moisture and contamination from affecting the reagent pads. Avoid storing the test strips near strong acids, bases, or other chemicals that might react with the reagents.
Always follow the storage instructions specified on the product packaging and the accompanying SDS. Regularly check the expiration date on the packaging and discard expired test strips appropriately.
Last Point
Mastering the use of Aquadur test strips empowers individuals and professionals alike to quickly and effectively assess water quality. By understanding the nuances of sample collection, test procedures, and result interpretation, users can confidently utilize these strips to monitor various water parameters. This guide has provided a thorough understanding of the process, emphasizing the importance of accuracy and safety throughout.
Remember, consistent application of these techniques will lead to reliable results and informed decisions regarding water quality management.
Question & Answer Hub
What happens if the test strip color doesn’t match the chart exactly?
If the color falls between two values on the chart, estimate the reading. Significant discrepancies may indicate a problem with the strip or the testing procedure. Repeat the test with a new strip.
How long are Aquadur test strips good for?
Check the expiration date printed on the container. Expired strips may provide inaccurate results.
Can I reuse Aquadur test strips?
No, Aquadur test strips are for single use only. Reusing them will compromise the accuracy of the results.
What should I do if I get a result indicating unsafe water?
Consult a water quality specialist or your local health authority for further testing and advice.
