35 Units of semaglutide is how many mg? This question highlights the crucial need for precise understanding of semaglutide dosage. Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, is prescribed for various conditions, including type 2 diabetes and weight management. However, its dosage isn’t expressed solely in milligrams (mg); it’s often given in units, which vary depending on the specific formulation and concentration.
Therefore, converting units to milligrams is essential for accurate medication administration and patient safety. This necessitates a clear understanding of the different semaglutide formulations available and their respective mg per unit values.
Understanding the relationship between units and milligrams is paramount for healthcare professionals and patients alike. Incorrect dosage can lead to ineffective treatment or adverse side effects. This discussion will delve into the different semaglutide formulations, explain the unit-to-milligram conversion process, and emphasize the importance of accurate dosage for optimal therapeutic outcomes. We will explore how various factors influence dosage decisions and address common misconceptions surrounding semaglutide administration.
Semaglutide Dosage Forms and Strengths
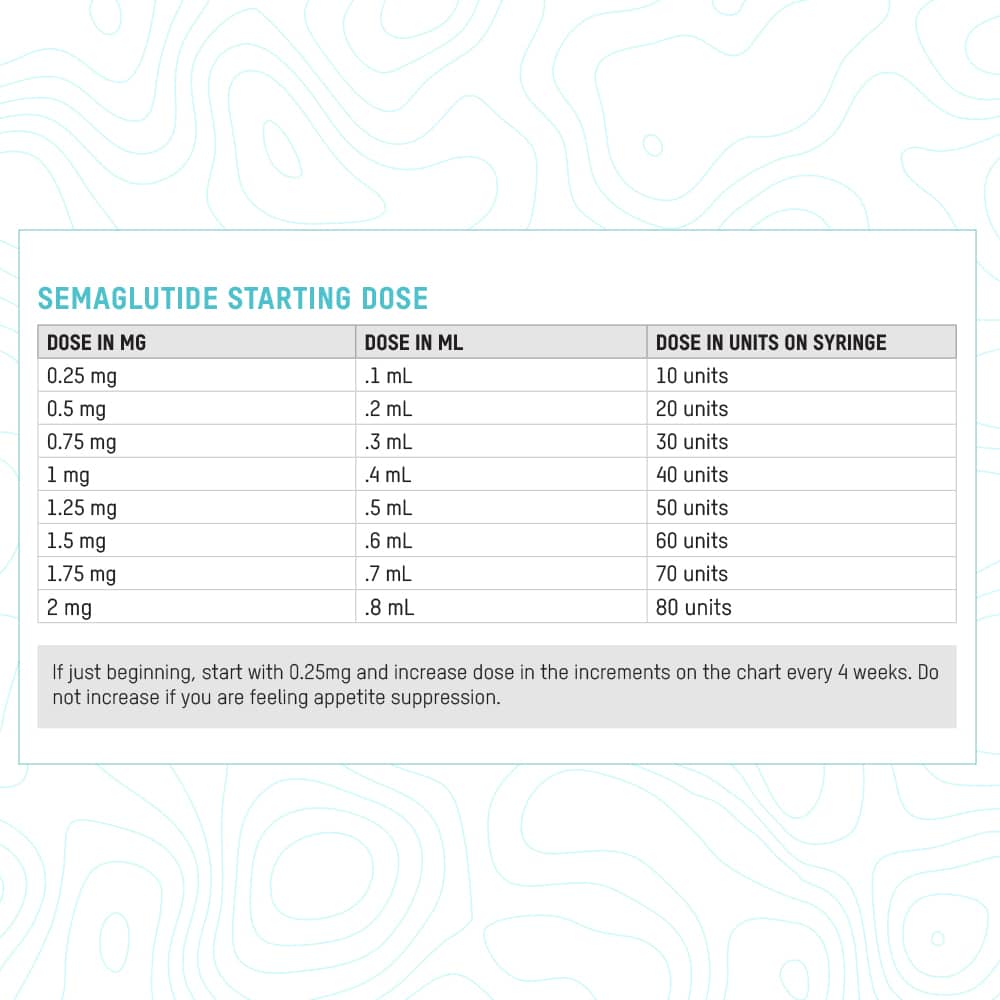
Semaglutide is available in several formulations, each with a specific concentration and delivery method. Understanding these differences is crucial for appropriate patient selection and safe administration. The following information details the available semaglutide products, their strengths, and packaging details. Note that specific product availability may vary by region and regulatory approvals.
Semaglutide Formulations and Strengths
The various semaglutide formulations offer different strengths and delivery methods to cater to diverse patient needs and preferences. The table below summarizes the key characteristics of commonly available semaglutide products. It’s important to consult the product labeling for the most up-to-date and accurate information.
| Formulation | Unit Size (mg) | mg per Unit | Total mg per Package |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ozempic® (pre-filled pen) | 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg | 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg | 4 (0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg pens) |
| Rybelsus® (oral tablet) | 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7 mg, 14 mg | 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7 mg, 14 mg | 30 tablets (2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7 mg, 14 mg) |
| Wegovy® (pre-filled pen) | 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 1.7 mg, 2 mg | 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 1.7 mg, 2 mg | 4 (0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 1.7 mg, 2 mg pens) |
Concentration Differences Between Semaglutide Products
Significant concentration differences exist between various semaglutide products. Ozempic ® and Wegovy ®, both injectable formulations, utilize similar strengths (though not identical) delivered via pre-filled pens. However, Rybelsus ®, an oral formulation, offers higher mg per unit dosages compared to the injectable options. These differences reflect the distinct routes of administration and pharmacokinetic profiles of each formulation. The lower concentrations in Ozempic ® and Wegovy ® are typically used for titration purposes at the start of treatment.
Packaging Information for Semaglutide Formulations
The packaging for each semaglutide formulation typically includes the number of units specified above. Each pen or package of tablets is clearly labeled with the concentration, total number of doses, and necessary storage instructions. This information is vital for patients to correctly administer the medication and ensure its efficacy and safety. It is crucial to follow the instructions carefully to prevent medication errors.
Calculating Total Semaglutide Dosage: 35 Units Of Semaglutide Is How Many Mg
Determining the total milligrams of semaglutide in a given number of units requires knowing the concentration of the specific formulation being used. This calculation is crucial for accurate dosing and patient safety. The concentration varies depending on the brand and presentation of the semaglutide product.
The following steps Artikel a method to calculate the total milligrams of semaglutide from a given number of units.
Determining the milligram equivalent of 35 units of semaglutide requires knowing the concentration of the specific medication being used, as it varies. This is analogous to understanding the precise application process for a vehicle’s aesthetic modification, such as figuring out how to properly install a wood decal, as detailed in this guide: 04 pt cruiser woody how is the wood decal installed.
Both scenarios necessitate precise information for accurate results; therefore, consulting the semaglutide packaging is crucial to convert units to milligrams.
Step-by-Step Calculation Method
To accurately calculate the total milligrams of semaglutide from a given number of units, follow these steps:
- Identify the formulation: Determine the specific brand and presentation of semaglutide (e.g., Ozempic, Wegovy, Rybelsus). This is crucial because the concentration (mg/unit) varies between formulations.
- Determine the mg per unit: Find the concentration of the semaglutide formulation in milligrams per unit (mg/unit). This information is typically found on the product label or package insert.
- Multiply units by mg/unit: Multiply the number of units (in this case, 35) by the mg/unit value obtained in step 2. This calculation yields the total milligrams of semaglutide.
Examples of Semaglutide Dosage Calculations, 35 units of semaglutide is how many mg
The following table illustrates the total milligrams of semaglutide in 35 units for different formulations. Note that these values are examples and may not represent all available formulations or strengths. Always refer to the product labeling for accurate mg/unit information.
| Formulation | Units | mg per Unit | Total mg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Formulation A | 35 | 2 mg | 70 mg |
| Example Formulation B | 35 | 1 mg | 35 mg |
| Example Formulation C | 35 | 0.5 mg | 17.5 mg |
Converting Units to Milligrams in Different Scenarios
Accurate conversion from units to milligrams is essential for safe and effective semaglutide administration. The process remains consistent across various scenarios, always relying on the known concentration (mg/unit) of the specific product.
For instance, if a patient is prescribed 28 units of a semaglutide formulation with a concentration of 1.5 mg/unit, the total semaglutide dosage would be calculated as follows: 28 units
– 1.5 mg/unit = 42 mg. Similarly, if a different formulation contains 0.25 mg/unit and a patient receives 50 units, the total dosage would be: 50 units
– 0.25 mg/unit = 12.5 mg.
It is crucial to always double-check the mg/unit value on the medication label before performing these calculations. Incorrect calculations could lead to improper dosing and potential adverse effects.
Factors Affecting Semaglutide Dosage
Semaglutide dosage is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Healthcare professionals carefully consider several factors to determine the appropriate starting dose and subsequent adjustments for each individual patient. This ensures optimal therapeutic benefit while minimizing potential adverse effects. These factors are interconnected and require careful clinical judgment.
The primary considerations when prescribing semaglutide include the patient’s weight, specific medical condition being treated, pre-existing medical history, and the patient’s response to the medication. Adjustments are made based on individual tolerability and the achievement of therapeutic goals, such as weight loss or improved glycemic control. The interplay of these factors is crucial in determining the optimal semaglutide regimen for each patient.
Patient Weight and Body Mass Index (BMI)
Patient weight and BMI are significant determinants of semaglutide dosage, particularly in the context of weight management. Higher BMI generally necessitates a higher starting dose and potentially a more rapid titration to the target dose. However, it’s crucial to note that weight alone isn’t the sole factor; individual response to the medication is also a key consideration. For instance, a patient with a high BMI who experiences significant gastrointestinal side effects at a higher dose might require a slower titration or a lower maintenance dose.
Medical History and Comorbidities
A comprehensive medical history is essential before initiating semaglutide therapy. Patients with a history of pancreatitis, severe gastrointestinal disorders, or a family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) may require careful monitoring or may be unsuitable candidates for semaglutide treatment. Pre-existing conditions like kidney disease may also influence dosage adjustments due to the drug’s excretion pathways. For example, patients with moderate to severe kidney impairment may require dose reduction to prevent accumulation and potential adverse events.
Response to Treatment
Regular monitoring of treatment response is vital. This involves tracking weight loss (if applicable), glycemic control (HbA1c levels), and the occurrence of any adverse effects. If a patient is not achieving the desired therapeutic goals despite being on a higher dose, alternative treatment strategies might be considered. Conversely, if a patient experiences significant side effects at a particular dose, a dose reduction might be necessary.
The physician will carefully balance the benefits of continued treatment with the potential risks of side effects.
Risks Associated with Exceeding Recommended Dosage
Exceeding the recommended semaglutide dosage significantly increases the risk of adverse effects. Common side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation, are often dose-related and can become more severe at higher doses. More serious adverse events, including pancreatitis and gallbladder problems, have also been reported, although the risk remains relatively low within the recommended dosage range. Therefore, strict adherence to the prescribed dosage and careful monitoring are crucial to minimize potential risks.
Dosage Variations Across Medical Conditions
Semaglutide is approved for several indications, including type 2 diabetes and obesity. Dosage regimens may vary slightly depending on the specific condition being treated and the patient’s individual characteristics. For example, the starting dose and titration schedule for weight management may differ from those used for glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. However, the underlying principles of individualization based on weight, medical history, and response to treatment remain consistent across all indications.
A healthcare professional will determine the appropriate regimen based on the patient’s specific needs and clinical presentation.
Understanding Semaglutide Units
Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, is not measured in milligrams (mg) like many other medications. Instead, its dosage is expressed in units, a measure that reflects the biological activity of the drug. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurate dosing and safe administration.Semaglutide units are a measure of the amount of biologically active semaglutide present in a given formulation.
One unit does not directly equate to a specific weight in milligrams. The relationship between units and milligrams is determined during the manufacturing process and is specific to each formulation of semaglutide (e.g., Ozempic, Wegovy). This means that a 1 mg semaglutide tablet would not contain the same number of units as a 1 mg semaglutide injection. Therefore, it’s inappropriate to directly convert between units and milligrams without knowing the specific formulation.
Semaglutide Unit-Milligram Relationship
Imagine a bar graph. The horizontal axis represents different semaglutide formulations (e.g., Ozempic pen, Wegovy injection). The vertical axis represents the number of units. Each bar represents a specific formulation, and its height corresponds to the number of units contained in a standard dose (e.g., 0.25mg, 0.5mg, 1mg, 2mg) of that particular formulation. Crucially, the bar heights would vary significantly, illustrating that the same weight (in milligrams) of semaglutide across different formulations does not translate to the same number of units.
This is because the formulation process influences the concentration and bioavailability of the active ingredient. For instance, one formulation might have a higher concentration of semaglutide per milligram compared to another, leading to a different number of units. This visual representation highlights the importance of using the units provided on the specific semaglutide product labeling, rather than attempting a conversion from milligrams.
Semaglutide Delivery and Unit Measurement
Semaglutide is primarily administered via subcutaneous injection using pre-filled pens or syringes. The dosage, expressed in units, is precisely measured using the pre-set mechanisms within the injection device. These devices are designed to deliver a specific number of units with each injection, eliminating the need for manual measurement. The units are calibrated during the manufacturing process, ensuring that each injection delivers the intended amount of biologically active semaglutide.
The injection site (usually the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm) should be rotated with each injection to minimize potential irritation or injection site reactions. The dosage and frequency of injection are determined by a healthcare professional based on individual patient needs and response to treatment. Improper administration or attempts to convert units to milligrams without proper understanding of the formulation-specific relationship could lead to inaccurate dosing and ineffective treatment.
Array
Maintaining the precise dosage of semaglutide as prescribed by a healthcare professional is crucial for effective weight management and diabetes control, while minimizing potential adverse effects. Deviation from the recommended dose can significantly impact treatment outcomes and increase the risk of experiencing undesirable side effects.Semaglutide, like other medications, operates within a specific therapeutic window. This means there’s a range of dosage where the drug is most effective and safe.
Taking less than the prescribed dose may result in insufficient therapeutic effects, meaning the medication may not effectively manage blood sugar or promote weight loss. Conversely, exceeding the prescribed dose can lead to an increased risk of adverse events and does not necessarily translate to enhanced benefits. The body’s response to medication is complex and non-linear; a higher dose doesn’t always equate to a proportionally better outcome.
Potential Side Effects of Incorrect Semaglutide Dosage
Incorrect semaglutide dosage can lead to a range of side effects, varying in severity depending on the extent of the deviation and individual patient factors. Taking too little semaglutide might lead to a lack of improvement in blood sugar control or weight loss, essentially rendering the treatment ineffective. Conversely, taking too much semaglutide increases the risk of experiencing more severe gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation.
These side effects can be significantly more pronounced at higher doses. Additionally, pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) is a rare but serious side effect that is more likely to occur with higher doses or misuse of the medication. Other potential side effects associated with incorrect dosage include gallbladder problems and kidney problems. It’s crucial to remember that individual responses to medication can vary.
Ensuring Correct Semaglutide Dosage
Several strategies can help patients ensure they are taking the correct dose of semaglutide. First and foremost, patients should meticulously follow their healthcare provider’s instructions. This includes understanding the prescribed dosage, the frequency of administration, and the correct method of injection. Patients should clearly communicate any questions or concerns they have about their medication to their doctor or pharmacist.
They should also carefully review the medication label and package insert for any instructions or warnings. Using a medication organizer or setting reminders can help ensure that doses are taken at the correct time. Patients should also report any unusual side effects or concerns to their healthcare provider immediately. Accurate self-monitoring of blood glucose levels (if applicable) and regular weigh-ins can help assess the effectiveness of the treatment and alert patients or their healthcare providers to any potential issues.
Finally, maintaining open communication with the healthcare team is vital for adjusting the dosage if necessary and ensuring optimal treatment.
Accurate semaglutide dosage is critical for effective treatment and minimizing potential risks. Converting units to milligrams requires knowledge of the specific formulation’s concentration. This process, while seemingly simple, demands precision to ensure patient safety and therapeutic efficacy. Understanding the factors influencing dosage decisions, such as patient weight and medical history, is crucial for healthcare professionals. Patient education and adherence to prescribed dosages are key to successful semaglutide therapy.
Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized dosage recommendations and to address any concerns regarding semaglutide medication.
Quick FAQs
What are the potential side effects of incorrect semaglutide dosage?
Incorrect dosage can lead to both under-treatment (ineffective glucose control or weight loss) and over-treatment (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pancreatitis, and other more serious adverse events).
Can I convert units to milligrams myself without consulting a doctor?
While the conversion itself is a mathematical process, it’s crucial to understand that the appropriate dosage is determined by a healthcare professional considering individual factors. Self-calculating dosage is strongly discouraged.
Where can I find the mg per unit information for my specific semaglutide formulation?
This information is available on the medication packaging, the medication insert, or from your pharmacist or healthcare provider.
What if I accidentally take a higher or lower dose of semaglutide than prescribed?
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you suspect you have taken an incorrect dose. They will provide guidance based on your situation.
