20 units of tirzepatide is how many mg? This question highlights the crucial need for accurate dosage calculation in managing type 2 diabetes and obesity. Tirzepatide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonist, is administered via injection, and its dosage is determined by the concentration of the specific formulation. Understanding the conversion from units to milligrams is essential for healthcare professionals and patients to ensure safe and effective treatment.
This guide provides a clear and comprehensive explanation of this conversion, along with practical examples and considerations for safe medication administration.
The potency of tirzepatide injections varies depending on the manufacturer and formulation. Accurate conversion from units to milligrams requires knowing the precise concentration (mg/mL) of the specific injection being used. This guide will detail the process of calculating the milligram equivalent of a given unit dose, emphasizing the importance of verifying the concentration before performing any calculations. We will also explore the potential consequences of dosage errors and provide strategies for safe and accurate medication administration.
Understanding Tirzepatide Dosage
Tirzepatide is a prescription medication administered via subcutaneous injection used to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. Understanding the appropriate dosage is crucial for maximizing its therapeutic benefits and minimizing potential side effects. Dosage is not a one-size-fits-all approach and requires careful consideration of individual patient factors.
Tirzepatide Injection Strengths
Tirzepatide is available in several pre-filled injection pen strengths, allowing for titration to achieve optimal glycemic control. These varying strengths enable healthcare providers to tailor treatment based on individual patient needs and responses. The precise strengths offered may vary by region, so it is essential to consult the prescribing information specific to your location.
Factors Influencing Tirzepatide Dosage
Several factors influence the prescribed dose of tirzepatide. These factors are carefully considered by healthcare professionals to create a personalized treatment plan. Weight, baseline blood glucose levels, and the presence of other medical conditions are key determinants.
Tirzepatide Injection Strengths and Corresponding Mg Amounts
The following table illustrates the available strengths of tirzepatide injections and their corresponding milligram amounts. Please note that this information is for illustrative purposes and may not reflect all strengths available in all regions. Always refer to the product labeling for the most up-to-date and accurate information.
The conversion of 20 units of tirzepatide to milligrams depends on the concentration of the specific tirzepatide injection pen being used. This is because the concentration varies. Consider this in relation to visualizing a length; for example, understanding 2 inches how long helps illustrate the need for precise measurements. Therefore, always refer to your prescription or the medication packaging to determine the mg per unit for accurate dosage calculation of 20 units of tirzepatide.
| Injection Strength (mg/mL) | Presentation (mL) | Total mg per Injection | Typical Starting Dose (mg/week) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5 | 0.5 | 1.25 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 5 |
| 10 | 0.5 | 5 | 10 |
| 15 | 0.5 | 7.5 | 15 |
Calculating Tirzepatide Dosage
Converting units of tirzepatide to milligrams requires knowing the concentration of the medication in the injection. This calculation is crucial for accurate administration and ensuring patient safety. Incorrect dosage can lead to ineffective treatment or adverse effects.
Converting Units to Milligrams
To convert 20 units of tirzepatide to milligrams, we need the concentration of the injection. Let’s assume the concentration is 2.5 mg/mL. This means that there are 2.5 milligrams of tirzepatide in every 1 milliliter of solution. However, we are given the dosage in units, not milliliters. Therefore, we need additional information to complete the conversion.
This information is typically found on the medication’s label or package insert. Let’s assume, for the purpose of this example, that each 1 mL of the solution contains 100 units of tirzepatide.This additional information allows us to perform a two-step conversion. First, we convert units to milliliters, then milliliters to milligrams.Step 1: Convert units to milliliters.If 100 units = 1 mL, then 20 units = (20 units / 100 units/mL) = 0.2 mLStep 2: Convert milliliters to milligrams.If 2.5 mg = 1 mL, then 0.2 mL = (0.2 mL
2.5 mg/mL) = 0.5 mg
Therefore, 20 units of tirzepatide at a concentration of 2.5 mg/mL (with 100 units/mL) is equivalent to 0.5 mg.
Formula for Unit to Milligram Conversion
The formula for converting units of tirzepatide to milligrams is:
mg = (Units / Units per mL)
mg per mL
Where:* mg = milligrams of tirzepatide
- Units = the number of units of tirzepatide
- Units per mL = the number of units of tirzepatide per milliliter of solution
- mg per mL = the number of milligrams of tirzepatide per milliliter of solution
Text-Based Calculator for Tirzepatide Conversion
To use this calculator, input the values as prompted.Enter the number of units of tirzepatide: [User Input: Units]Enter the concentration of the injection in units per mL: [User Input: Units/mL]Enter the concentration of the injection in mg per mL: [User Input: mg/mL]Calculation: ( [Units] / [Units/mL] )
[mg/mL] = [Result
mg]The result will be the equivalent milligrams of tirzepatide. Remember to always verify the concentration values with the medication’s labeling.
Variations in Tirzepatide Concentration
Tirzepatide is available in various concentrations, and understanding these differences is crucial for accurate dosage calculation and safe administration. Incorrect concentration selection can lead to significant dosing errors, potentially impacting treatment efficacy and patient safety. This section will detail the commercially available concentrations and their implications for dosage calculations.The commercially available concentrations of tirzepatide injection differ across regions and may change over time.
Therefore, always refer to the product labeling for the precise concentration of the specific vial or pen being used. However, common concentrations include 2.5 mg/mL, 15 mg/mL, and potentially others depending on the specific formulation and market availability. These variations necessitate careful attention to detail when calculating the required dose in units.
Concentration Impact on Dosage Calculation
Different concentrations directly affect the conversion between units and milligrams. For example, a prescription of 20 units of a 2.5 mg/mL tirzepatide solution would require a different volume calculation than a 20-unit prescription of a 15 mg/mL solution. The number of units remains constant, but the concentration alters the amount of solution needed to deliver that specified unit dose.
To illustrate, let’s assume a hypothetical scenario where each unit of tirzepatide delivers a consistent amount of active drug, say 0.25 mg.In a 2.5 mg/mL solution, 20 units (20 units0.25 mg/unit = 5 mg) would require 2 mL of solution (5 mg / 2.5 mg/mL = 2 mL). Conversely, in a 15 mg/mL solution, the same 20 units (5 mg) would require only 0.33 mL (5 mg / 15 mg/mL = 0.33 mL) of solution.
This demonstrates the importance of carefully considering the concentration when calculating the required volume of tirzepatide for injection. Using the wrong concentration in the calculation will result in an incorrect dosage.
Importance of Concentration Verification
Verifying the concentration of the tirzepatide injection before calculating the dosage is paramount. Failure to do so can lead to significant dosing errors, resulting in either underdosing or, more critically, overdosing. Underdosing might reduce the therapeutic effect, while overdosing could lead to adverse events. Always cross-check the concentration indicated on the vial or pen label with the prescription order to ensure they match.
Double-checking this information is a critical step in ensuring patient safety and treatment effectiveness. Any discrepancies should be immediately clarified with the prescribing physician or pharmacist before administering the medication.
Clinical Implications of Dosage Calculation: 20 Units Of Tirzepatide Is How Many Mg
Accurate calculation and administration of tirzepatide are critical for patient safety and efficacy. Miscalculations can lead to serious adverse events, while underdosing may compromise therapeutic benefits. This section explores the potential consequences of dosage errors and Artikels strategies for accurate dosage administration.
The consequences of miscalculating tirzepatide dosage can range from mild to severe. Underdosing may result in inadequate glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes, potentially leading to complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis or worsening of existing diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, or neuropathy. Conversely, overdosing can cause significant gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation, potentially leading to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
In severe cases, pancreatitis or gallbladder problems have been reported. The severity of these consequences depends on the magnitude of the dosage error and the individual patient’s characteristics and overall health.
Consequences of Tirzepatide Dosage Errors
Several factors contribute to the risk of dosage errors. These include illegible prescriptions, misinterpretations of dosage instructions, and incorrect conversions between units of measurement (e.g., milligrams to micrograms). Furthermore, variations in the concentration of tirzepatide preparations (e.g., pre-filled pens with different concentrations) can increase the likelihood of errors if not carefully considered. The impact of these errors is magnified in patients with compromised renal or hepatic function, as their metabolism and clearance of tirzepatide may differ from those with normal function, potentially increasing the risk of adverse effects from both underdosing and overdosing.
Ensuring Accurate Dosage Calculation
Several critical steps are necessary to ensure accurate tirzepatide dosage calculation. These steps involve careful verification of the prescription, confirmation of the patient’s weight and renal function (where relevant), and accurate conversion of units if necessary. Double-checking calculations by an independent healthcare professional is also crucial. The use of standardized protocols and electronic prescribing systems can help minimize errors.
Checklist for Preventing Dosage Errors
A comprehensive checklist can serve as a valuable tool for healthcare professionals to prevent tirzepatide dosage errors. This checklist should be followed diligently at each stage of the medication administration process.
- Verify the prescription order: Confirm the patient’s identity, the prescribed dosage, and the frequency of administration.
- Check the concentration of the tirzepatide preparation: Ensure that the concentration of the pre-filled pen or vial matches the prescribed dosage.
- Calculate the dosage accurately: Perform the calculation independently and have another healthcare professional verify the result.
- Document the administration: Record the date, time, dosage administered, and any observed side effects.
- Educate the patient: Provide clear instructions on how to administer the medication and what to watch for.
- Monitor for adverse events: Carefully observe the patient for any signs or symptoms of adverse events and report them immediately.
- Utilize technology: Leverage electronic prescribing systems and automated dispensing systems to reduce the risk of manual errors.
Array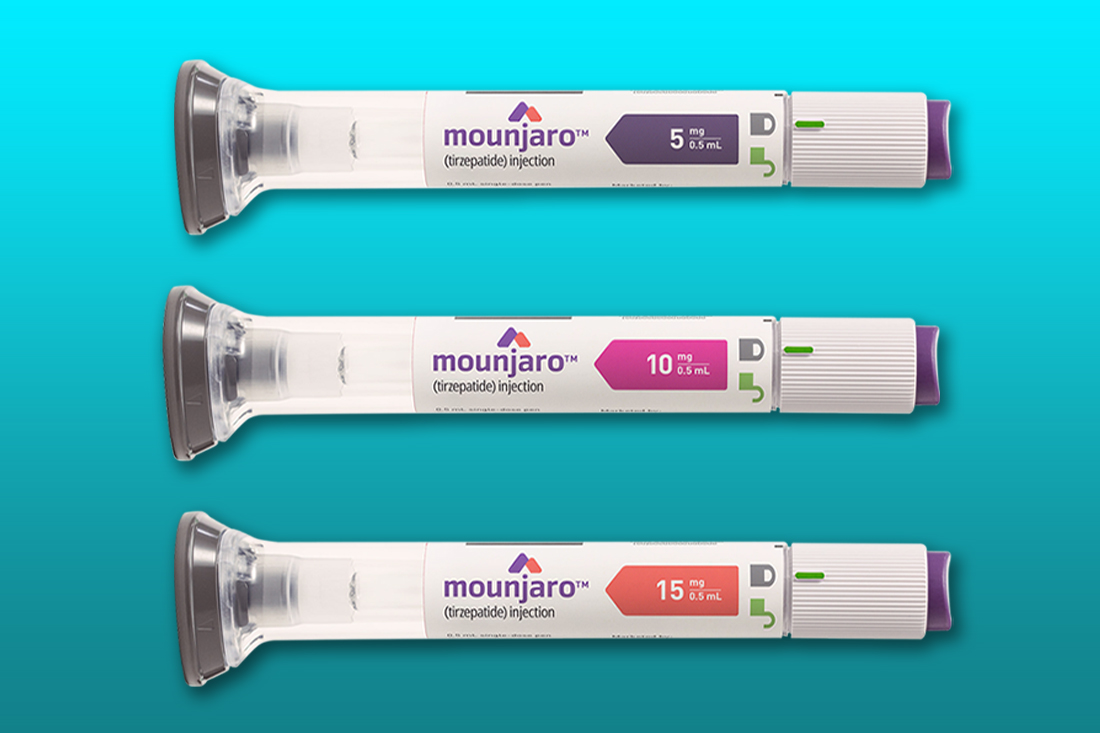
Accurate dosage calculation is crucial for effective tirzepatide therapy. Incorrect dosing can lead to suboptimal glycemic control or adverse events. The following examples demonstrate dosage calculations using different concentrations, emphasizing the importance of careful attention to detail.
Tirzepatide Dosage Calculation Examples
This section provides three detailed examples of tirzepatide dosage calculations, each using a different concentration. The calculations are presented step-by-step to ensure clarity and understanding.
Example 1: 2.5 mg/0.5 mL concentration
A patient requires a 5 mg dose of tirzepatide. The available pen contains 2.5 mg of tirzepatide per 0.5 mL of solution. To determine the required volume, we use the following calculation:
(Desired dose / Concentration) x Volume per dose = Volume to administer
(5 mg / 2.5 mg/0.5 mL) x 0.5 mL = 1 mL
Therefore, the patient should be administered 1 mL of the 2.5 mg/0.5 mL tirzepatide solution.
Example 2: 5 mg/1 mL concentration
A patient requires a 7.5 mg dose of tirzepatide. The available pen contains 5 mg of tirzepatide per 1 mL of solution. The calculation is as follows:
(Desired dose / Concentration) = Volume to administer
(7.5 mg / 5 mg/1 mL) = 1.5 mL
Therefore, the patient should be administered 1.5 mL of the 5 mg/1 mL tirzepatide solution.
Example 3: 15 mg/1.5 mL concentration
A patient requires a 10 mg dose of tirzepatide. The available pen contains 15 mg of tirzepatide per 1.5 mL of solution. The calculation is:
(Desired dose / Concentration) x Volume per dose = Volume to administer
(10 mg / 15 mg/1.5 mL) x 1.5 mL = 1 mL
Therefore, the patient should be administered 1 mL of the 15 mg/1.5 mL tirzepatide solution.
Tirzepatide Injection Pen Visual Representation
Tirzepatide injection pens typically feature a digital display showing the remaining dose in units. The pen body usually has markings indicating the number of units selected for injection. A dose selection dial or button allows the user to choose the desired number of units. The pen will then deliver the selected dose when the injection button is pressed.
The unit markings are clearly visible and increment in consistent steps (e.g., 0.25 units, 0.5 units, or 1 unit increments, depending on the pen’s design). The user should always carefully check the selected dose before injection to ensure accuracy.
Syringe Dosage Illustration, 20 units of tirzepatide is how many mg
This section describes a visual representation of a syringe with graduated markings for drawing up a specific dosage of tirzepatide. While a specific concentration isn’t specified, the example assumes a concentration requiring a 1.25 mL draw.+—————–+| || 1.5 mL || || 1.0 mL || || 0.75 mL || || 0.5 mL || || 0.25 mL || || 0 mL |+—————–+
The syringe above is a hypothetical representation. The markings show the volume in mL. To draw up 1.25 mL, the plunger should be drawn to the line exactly between the 1.0 mL and 1.5 mL markings.
Accurate calculation of tirzepatide dosage is paramount for optimal therapeutic outcomes and patient safety. Miscalculations can lead to suboptimal treatment or adverse effects. This guide has demonstrated the process of converting units to milligrams, emphasizing the importance of verifying the injection concentration and performing calculations carefully. By understanding the principles Artikeld here, healthcare professionals and patients can work together to ensure the safe and effective administration of tirzepatide.
Top FAQs
What happens if I accidentally inject too much tirzepatide?
Overdosing on tirzepatide can lead to nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect an overdose.
Can I use a different concentration of tirzepatide than prescribed?
No. Always use the concentration of tirzepatide prescribed by your doctor. Changing the concentration without medical supervision can be dangerous.
How do I dispose of used tirzepatide pens and needles?
Dispose of used needles and pens according to your local regulations. Usually, this involves placing them in a puncture-resistant container and disposing of it properly.
What are the common side effects of tirzepatide?
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and decreased appetite. More serious side effects are rare but possible.
