1992 vette rear monspring how many spacer – 1992 Vette rear monospring: how many spacers? This question is central to understanding the ride height and handling of this iconic sports car. The 1992 Corvette’s rear suspension, featuring a monospring setup, allows for adjustments to achieve optimal performance. Understanding the role of spacers, their various types, and the method for determining the correct number is crucial for maintaining or modifying the vehicle’s handling characteristics.
This guide will explore the intricacies of the 1992 Corvette’s rear monospring system, focusing specifically on the use and impact of spacers.
The rear monospring system in the 1992 Corvette is a key component of its performance. It consists of the monospring itself, various mounting hardware, and potentially, spacers. Spacers are used to alter the ride height, affecting both the vehicle’s appearance and its handling. Improper use or installation of spacers can negatively impact performance, leading to issues such as poor handling, uneven tire wear, and potential damage to suspension components.
This guide will detail the correct procedures for determining the appropriate number of spacers needed and provide insights into the potential consequences of incorrect installation.
1992 Corvette Rear Monospring Basics: 1992 Vette Rear Monspring How Many Spacer
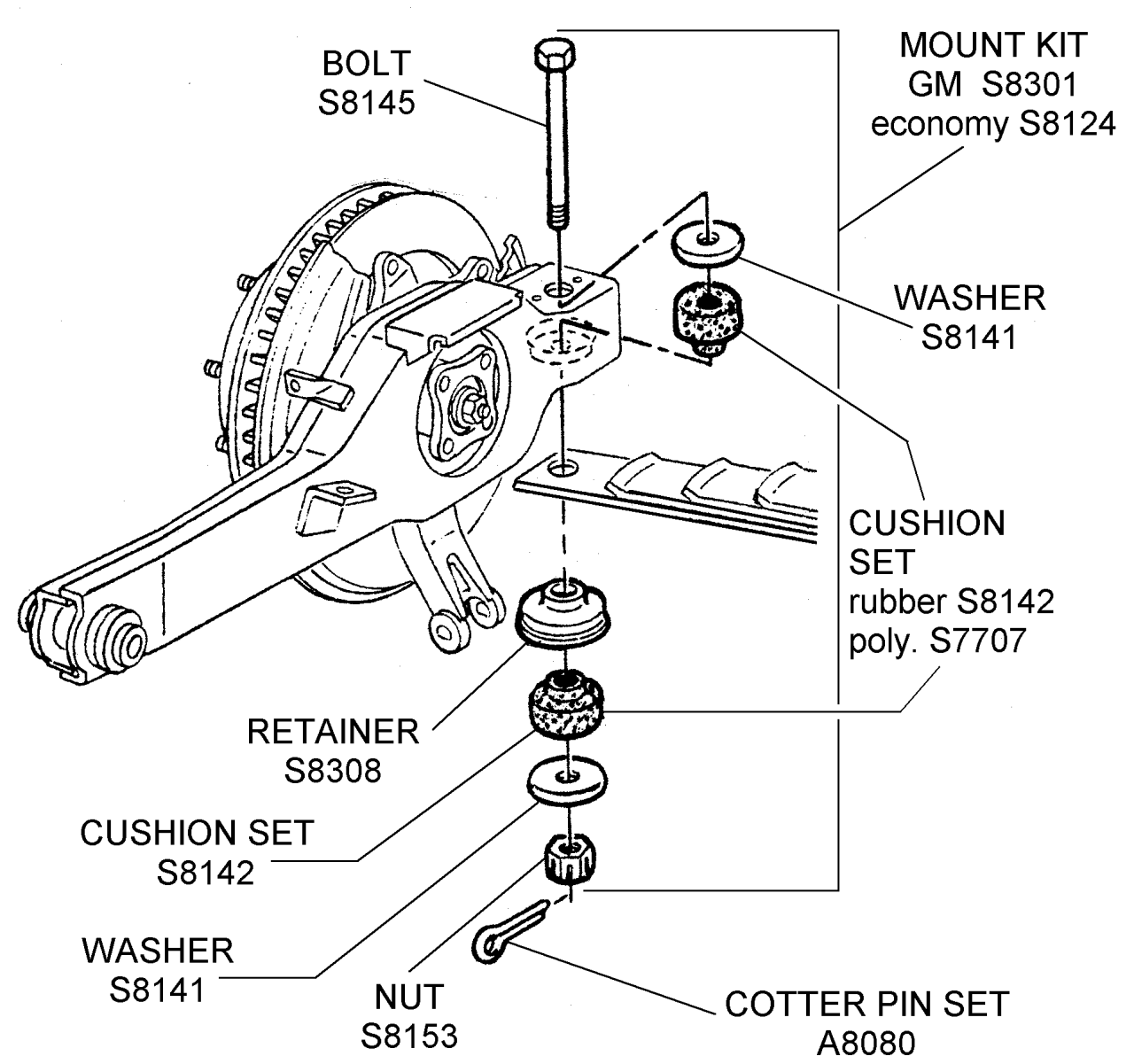
The 1992 Chevrolet Corvette featured a unique rear suspension system utilizing a single, large leaf spring, commonly referred to as a monospring, to locate and support the rear axle. This design, while unconventional compared to more common multi-link or independent setups, offered a balance of simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and surprisingly good handling characteristics for its time. Understanding its function and potential failure points is crucial for maintaining the performance and reliability of a classic C4 Corvette.The rear monospring in a 1992 Corvette serves a dual purpose: it acts as the primary spring element, absorbing shocks and bumps from the road, and it also locates the rear axle laterally, controlling its movement side-to-side.
This contrasts with independent rear suspensions where separate components handle these functions. The monospring’s design, with its inherent stiffness, contributes to the Corvette’s characteristic handling, particularly its ability to rotate quickly and precisely through corners.
Components of the 1992 Corvette Rear Suspension System Related to the Monospring
The rear suspension system related to the monospring includes several key components working in concert. The monospring itself is a large, curved leaf spring made of steel. It’s anchored at its front end to the chassis via a mounting bracket and at its rear end to the differential housing using another bracket and mounting hardware. Shock absorbers are connected to the chassis and the differential housing, damping the spring’s oscillations.
A stabilizer bar (sway bar) further helps control body roll during cornering, connected to the differential housing and the chassis. Bushings and various mounting hardware connect these components, allowing for controlled movement while minimizing unwanted noise and vibration. Finally, the rear axle is a live axle, directly connected to the differential housing, and its location and movement are directly controlled by the monospring.
Typical Wear and Tear Patterns Observed in the Rear Monospring and its Associated Components
Over time, several components within the 1992 Corvette’s rear monospring suspension system are prone to wear. The monospring itself can fatigue and develop cracks, particularly at its mounting points where stress is concentrated. This can lead to a noticeable degradation in ride quality and handling. The bushings, which provide a compliant connection between the monospring and other components, tend to wear out, causing increased noise, clunking, and potentially affecting alignment.
The shock absorbers, responsible for damping oscillations, lose their effectiveness over time, leading to a bouncy ride and reduced control. The stabilizer bar bushings can also wear, reducing the effectiveness of the sway bar in controlling body roll. Finally, the mounting hardware itself can corrode or loosen, resulting in instability and potentially dangerous conditions. Regular inspection and replacement of worn components are vital to maintaining a safe and well-handling vehicle.
Installation and Adjustment Procedures
Installing or removing spacers from a 1992 Corvette’s rear monospring assembly requires careful attention to detail to ensure proper alignment and vehicle handling. Incorrect installation can lead to compromised handling, premature wear, and even damage to the suspension components. This section details the steps involved, best practices, and potential problems.
Spacer Installation and Removal
The process of installing or removing rear monospring spacers on a 1992 Corvette involves accessing the rear suspension components. This typically requires jacking up the vehicle securely, supporting it on jack stands, and removing relevant suspension components to gain access to the monospring. Spacers are typically installed between the monospring and the chassis or other suspension components. The specific location and method will depend on the type of spacer and the design of the suspension.
Always consult a detailed service manual specific to your 1992 Corvette model for precise instructions and torque specifications. Improper torque can lead to fastener failure or damage to the suspension. Each step should be executed methodically, using the correct tools and following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Removing spacers follows a reverse procedure of installation.
Ensuring Proper Alignment and Function
After installing or removing spacers, it’s crucial to ensure proper alignment and function of the rear suspension. This involves visually inspecting the components for correct placement and ensuring that all fasteners are properly tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. A post-installation alignment check by a qualified mechanic is strongly recommended. This alignment check will ensure that the vehicle’s wheels are correctly positioned relative to the chassis, minimizing tire wear and improving handling.
Any misalignment detected should be corrected before driving the vehicle. Failure to do so could lead to uneven tire wear, handling problems, and potentially dangerous driving conditions. Post-installation test driving should be done cautiously at low speeds to ensure that the suspension operates as intended.
Potential Problems and Solutions
Several problems might arise during spacer installation. One common issue is difficulty accessing the monospring due to limited space or interference from other components. Using specialized tools or employing creative techniques, such as using extensions or flexible wrenches, might be necessary. Another potential problem is damaging the threads on the fasteners during tightening or loosening. Using the correct size socket and applying even pressure will help prevent this.
Stripped threads might require helicoil inserts or other repair methods. Finally, incorrect spacer installation can lead to handling issues, such as instability or poor braking performance. If any problems occur, it’s advisable to consult a qualified mechanic or refer to the vehicle’s service manual. Improper installation could necessitate costly repairs.
Impact on Performance and Handling
Adding spacers to a 1992 Corvette’s rear monospring system alters the ride height and affects various aspects of its performance and handling characteristics. Understanding these changes is crucial for optimizing the vehicle’s behavior to suit individual preferences and driving styles. The impact is multifaceted, influencing acceleration, braking, and cornering capabilities.The primary effect of rear monospring spacers is a change in the vehicle’s center of gravity.
Increasing the ride height by adding spacers raises the center of gravity, which can negatively affect handling, particularly during cornering. Conversely, reducing ride height by removing or using thinner spacers lowers the center of gravity, potentially improving handling responsiveness. However, excessive lowering can negatively impact suspension travel and ride comfort. The interplay between ride height, tire contact patch, and suspension geometry dictates the overall performance changes.
Effect of Spacer Thickness on Acceleration, Braking, and Cornering, 1992 vette rear monspring how many spacer
Spacer thickness directly impacts the vehicle’s dynamic behavior. Thicker spacers, resulting in increased ride height, typically lead to slightly reduced acceleration due to increased unsprung weight and a higher center of gravity. Braking performance might also be marginally affected, potentially increasing stopping distances, although the impact is usually less pronounced than on acceleration. Cornering, however, is more significantly affected.
Increased ride height reduces stability and increases body roll, leading to less precise handling and a higher risk of oversteer. Conversely, thinner spacers (or the removal of spacers) lower the center of gravity, potentially improving acceleration, braking, and cornering. However, excessively low ride height can reduce suspension travel, negatively impacting ride comfort and potentially increasing the risk of bottoming out.
The optimal spacer thickness represents a compromise between handling, acceleration, braking, and ride comfort.
Comparative Analysis of Performance Differences Based on Spacer Thickness
The following table illustrates the potential performance differences based on varying spacer thicknesses. Note that these values are estimations and can vary depending on factors like tire pressure, driver skill, and road conditions. Actual results may deviate from these predictions.
| Spacer Thickness (inches) | Acceleration (0-60 mph) | Braking Distance (60-0 mph) | Cornering Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (No Spacers) | Slightly Improved | Slightly Improved | Improved |
| 0.5 | Minimal Change | Minimal Change | Slightly Reduced |
| 1.0 | Slightly Reduced | Slightly Reduced | Noticeably Reduced |
| 1.5 | Reduced | Reduced | Significantly Reduced |
Visual Representation of Spacer Placement

Understanding the precise location and orientation of spacers within the 1992 Corvette’s rear monospring assembly is crucial for proper installation and optimal performance. Incorrect placement can lead to handling issues, premature wear, and even damage to the suspension components. This section provides a detailed visual description, aiding in both installation and inspection.The rear monospring assembly utilizes spacers to adjust ride height and preload.
These spacers are cylindrical components, typically made of steel or aluminum, inserted between the monospring and the chassis mounting points. Their placement directly influences the spring’s effective length and, consequently, the vehicle’s ride height and handling characteristics.
Spacer Locations within the Rear Monospring Assembly
The primary spacer location is between the top of the monospring and the upper control arm mounting point on the chassis. A second, less common, spacer might be found between the bottom of the monospring and the lower control arm mounting point. These spacers are usually concentric with the monospring, meaning their central axis aligns perfectly with the monospring’s axis.
However, slight variations might exist depending on aftermarket modifications or specific spring designs. The orientation is generally straightforward; the spacers are placed flat against the mating surfaces to ensure even load distribution and prevent binding. Misalignment can result in uneven stress on the spring and surrounding components.
Visual Inspection of Spacers for Wear or Damage
Before installing or readjusting the rear monospring, a thorough visual inspection of the existing spacers is essential. This inspection helps identify potential problems that could compromise the suspension’s integrity and performance.A systematic approach is recommended. First, carefully remove the spacers from the assembly. Clean them thoroughly to remove any dirt, grime, or corrosion that might obscure potential damage.
Once clean, examine each spacer individually. Look for any signs of significant wear, such as excessive scoring, gouging, or deformation. Measure the diameter and height of each spacer using a caliper to check for dimensional changes indicative of wear or damage. Also, closely inspect the spacer’s surfaces for any cracks, fractures, or pitting. Pay particular attention to the contact surfaces, as these areas are most susceptible to wear.
Any spacer showing signs of significant wear, damage, or dimensional inconsistencies should be replaced immediately. Using damaged spacers can lead to unpredictable handling characteristics and potential safety hazards.
Array
Incorrect installation or improper use of spacers on a 1992 Corvette’s rear monospring can lead to several handling and ride quality problems. Addressing these issues requires a systematic approach, focusing on identifying the root cause and implementing appropriate corrective actions. This section details common problems and provides troubleshooting steps for resolving them.
Ride Height Discrepancies
Uneven ride height after spacer installation is a common issue. This could result from incorrectly positioned spacers, uneven weight distribution, or damaged suspension components. To diagnose the problem, carefully measure the ride height at each corner of the vehicle using a measuring tape and a level surface. Compare these measurements to the factory specifications or the desired ride height after spacer installation.
Significant deviations indicate a problem with spacer placement or other suspension components. If the discrepancy is significant, it is crucial to re-check spacer placement and ensure all suspension components are in good working order. If the problem persists, a professional alignment and suspension inspection might be necessary.
Poor Handling and Instability
Incorrect spacer height can negatively impact handling and stability. Excessive lift might lead to body roll, oversteer, or a vague steering feel, while insufficient lift may not achieve the desired effect. This is often due to an improper selection of spacer height or incorrect installation. Troubleshooting should involve verifying spacer height against the intended specification and checking for any binding or interference in the suspension system.
If the handling remains poor after correcting the spacer installation, it’s recommended to have a professional alignment performed to ensure the suspension geometry is correctly set. This may also reveal other underlying suspension issues.
Noise and Vibration
Unusual noises, such as clunking or rattling, after spacer installation may indicate loose components or parts rubbing against each other. This could stem from improperly tightened bolts, loose spacers, or components that are now contacting due to the altered ride height. A thorough inspection of all suspension components and their fasteners is crucial. Pay close attention to the areas where the spacers are installed and ensure all bolts are securely tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Addressing any loose parts or rubbing components should eliminate these noises. If the noises persist, further investigation of the suspension system might be needed.
Spacer Damage or Deformation
Over time or under heavy loads, spacers can deform or become damaged. This can lead to changes in ride height, handling, and noise issues. Regularly inspect the spacers for any signs of damage, such as cracks, bends, or excessive wear. If damage is detected, replace the spacer immediately. Using damaged spacers can compromise the integrity of the suspension system and lead to safety hazards.
Consider using high-quality, durable spacers designed to withstand the stresses of the vehicle’s operation.
Modifying the ride height of a 1992 Corvette using rear monospring spacers requires careful consideration and precise measurement. Understanding the relationship between spacer thickness and ride height, as well as the impact on handling and performance, is crucial for achieving desired results without compromising safety or vehicle integrity. By following the procedures Artikeld in this guide, Corvette owners can confidently adjust their vehicle’s ride height, optimizing both its appearance and its on-road performance.
Remember to always prioritize safety and consult with a qualified mechanic if unsure about any aspect of the process.
Common Queries
What are the signs of a worn rear monospring?
Sagging ride height, unusual noises from the rear suspension, and noticeable handling differences compared to a similar vehicle.
Can I use different types of spacers together?
Generally, it’s best to use spacers of the same material and type to ensure consistent performance and avoid potential issues.
What tools are needed to install rear monospring spacers?
Appropriate jack stands, jack, wrenches, and possibly a torque wrench are essential for safe installation.
How often should I inspect my rear monospring and spacers?
Regular inspection during routine maintenance checks is recommended. Look for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion.
